| E001 | 1 | E | S |
| What maintenance checks must be done regularly on every paraglider? | |||
| 1 | Check for any material damage on the webbing where metal touches webbing as well as stitching | ||
| 1 | Inspect the canopy for any abrasive damage as well as a porosity test | ||
| 1 | Inspect the lines for damages on the outer sheeting as well as line length. Stretching of the lines to obtain normal length will sometimes be needed | ||
| -2 | Wash the canopy every 3 months | ||
| -1 | A Paraglider has to be pulled up at least every 6 months for a visual check | ||
| E002 | 1 | E | S |
| Which of the statements are true for Kevlar lines | |||
| 1 | Has best resistance to heat of all the line types | ||
| 1 | Does not stretch or shrink much | ||
| 1 | Can become brittle | ||
| 1 | Can damage through kinks, twists, etc. | ||
| 1 | Damage is usually difficult to see | ||
| 1 | Is sensitive to UV rays | ||
| -1 | Can shrink, especially when moist. | ||
| -1 | Can regain its original length after shrinkage. | ||
| -1 | Is robust (does not weaken extensively from kinks). | ||
| -1 | Has good UV resistance | ||
| E003 | 1 | E | B |
| What is Trim Speed? | |||
| 1 | Hands, toggles up, maximum speed , without using any accelerator | ||
| -1 | Measured Speed with Trim tabs set on maximum speed | ||
| -1 | Measured Speed with full accelarator applied | ||
| -1 | Minimum Speed to enable a safe landing | ||
| E004 | 1 | E | S |
| Which of the statements are true for Dyneema lines | |||
| 1 | Can shrink, especially when moist. | ||
| 1 | Can regain its original length after shrinkage. | ||
| 1 | Is robust (does not weaken extensively from kinks). | ||
| 1 | Has a good UV resistance. | ||
| 1 | Can get damaged sooner than Kevlar from heat. | ||
| 1 | Is about 1.5 times stronger than Kevlar. | ||
| 1 | Can over-stretch with extreme loads | ||
| -1 | Has best resistance to heat of all the line types | ||
| -1 | Has least resistance to UV rays. | ||
| -1 | Does not stretch or shrink much | ||
| E005 | 1 | E | B |
| A toggle is a | |||
| 1 | Handle to steer your Paraglider | ||
| -1 | The handle to throw your reserve | ||
| -1 | A switch on your vario | ||
| -1 | A metal clamp to connect the Paraglider with the harness | ||
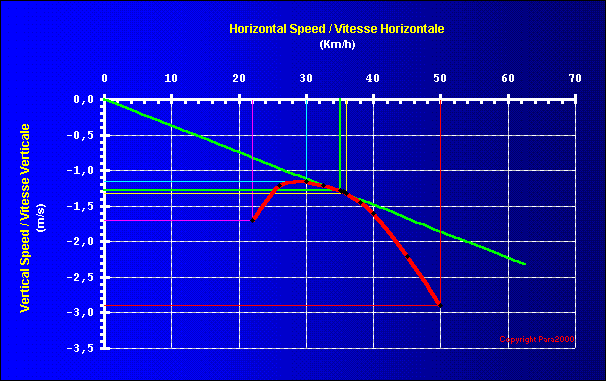
| E006 | 2 | E | S |
| What is the best glide ratio for this polare | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | at 36 km/h and 1.3 m/s, about 7.6 | ||
| -1 | at 50 km/h and 2.8 m/s , about 8 | ||
| -1 | at 22 km/h and 1.7 m/s , about 6.9 | ||
| -1 | at 30 km/h and 1.2 m/s , about 7.3 | ||
| http://parapente.para2000.free.fr/wings/index.html | |||
| E007 | 1 | E | S |
| What is a Hang Glider Category 3 according to CIVL? | |||
| 1 | A Paraglider | ||
| -1 | A weightshift Hang Glider | ||
| -1 | A Powered Paraglider | ||
| -1 | A control surface operated Hang Glider | ||
| E008 | 1 | E | S |
| Competition lines, also called dental floss, got a limited life span. Why? What should be done and what will happen if you do not do this? | |||
| 1 | Made of Kevlar which ages by bending and break | ||
| 1 | Have to be replaced after a manufacturer specified interval | ||
| 1 | Lines can break without indication of wear and tear in the air and you have a cascading effect of lines breaking. | ||
| -1 | This statement is wrong. all Paraglider lines are designed for infinite life | ||
| E009 | -1 | E | S |
| Cross braces in Paragliding are used for what? | |||
| 1 | Total load compensation and a better response to input | ||
| -1 | Connects the speed bar to the risers | ||
| -1 | Connects the risers to the harness | ||
| -1 | A device for tandem harnesses | ||
| E010 | 1 | E | S |
| The frequencies allocated for SAHPA pilots are | |||
| 1 | 141.600 MHz | ||
| 1 | 141.625 MHz | ||
| -1 | the same frequency as for any other aircraft | ||
| -1 | 144.600 MHz | ||
| E011 | 1 | E | S |
| The optimal aerial length for the 2m band 141.xxx frequencies used by SAHPA for hand held radios is | |||
| 1 | around 51 cm | ||
| -1 | around 15 cm | ||
| -1 | around 30 cm | ||
| -1 | around 25.5 cm | ||
| E012 | 1 | E | S |
| What does an Anemometer measure | |||
| 1 | Wind Speed | ||
| -1 | Humidity | ||
| -1 | Trigger temperature | ||
| -1 | Heating up of the ground layer | ||
| E013 | 1 | E | S |
| How is the weight load factor defined in a spiral? | |||
| 1 | Ratio of Apparent weight to all up weight. Usually expressed in G's | ||
| -1 | All up weight divided by glider area, kg/square meters | ||
| -1 | Difference between minimum and maximum clip in weight | ||
| -1 | Difference between flying with or without ballast | ||
| E014 | 1 | E | S |
| How does a Vario work? | |||
| 1 | By comparing successive measurements of atmospheric pressure | ||
| -1 | By measuring the temperature drop as you go higher | ||
| -1 | By measuring the airflow change around the device | ||
| -1 | By GPS based altitude changes | ||
| E015 | 1 | E | B |
| What is a cravat or cravattage? | |||
| 1 | French for bow-tie. Parts of your glider wing tips are entangled in the lines | ||
| -1 | A frontal collapse due to rotor which rolls up your canopy | ||
| -1 | An asymmetric B-Line stall, resulting in a negative spin | ||
| -1 | A maneuver to get out of a locked spiral | ||
| E016 | 1 | E | B |
| Which 3 AFNOR standards are used for paragliders? | |||
| 1 | Standard | ||
| 1 | Performance | ||
| 1 | Competition | ||
| -1 | 1 | ||
| -1 | 2 | ||
| -1 | 3 | ||
| E017 | 1 | E | B |
| The leading edge | |||
| 1 | has the A lines attached | ||
| 1 | got the cell openings | ||
| -4 | has the brake lines attached | ||
| 1 | is facing away from the pilot on the ground before take off | ||
| 1 | is facing into flying direction once airborne | ||
| E018 | 1 | E | S |
| 2m Band radios work best | |||
| 1 | with a direct line of sight | ||
| 1 | with no body parts or trees or other water containing objects in between | ||
| -1 | with good ionosphere conditions reflecting the waves | ||
| -1 | with the squelch turned on full | ||
| E019 | 1 | E | S |
| A GPS | |||
| 1 | has to be operated outdoors to work properly | ||
| 1 | needs movement to determine North and South | ||
| -1 | figures out from the earth rotation its location | ||
| -1 | uses the earth magnetic field | ||
| E020 | 1 | E | S |
| What options do you have when landing in strong wind , more than 40 km/h | |||
| 1 | C-Line landing | ||
| 1 | Do not flare , use your A's to collapse the canopy | ||
| -1 | Land as usual | ||
| -1 | B Line stall | ||
| E021 | 1 | E | S |
| A wet reserve | |||
| 1 | Should be opened immediately and hung out to dry out of the sun | ||
| 1 | get repacked after it has dried in the open | ||
| -1 | can stay in the container and dry there | ||
| -1 | Open the container but leave it packed and let it dry | ||
| E022 | 1 | E | S |
| How is the aspect ratio of a wing calculated? | |||
| 1 | Aspect ratio = wing span /chord length | ||
| -1 | Aspect ratio = chord length / wing span | ||
| 1 | Aspect ratio = (wing span * wing span) / wing area | ||
| -1 | Aspect ration = average line length / wing span | ||
| E023 | 1 | E | S |
| What does chord mean ? | |||
| 1 | a straight line connecting the leading edge tip of the profile with the trailing edge | ||
| -1 | the maximum circle radius that one can fit inside of a profile | ||
| -1 | the curve that is the center of all the circles that would make up the shape of a profile | ||
| -1 | the distance from the leading edge to the circle center of the maximum thickness of the profile | ||
| E024 | 1 | E | S |
| What particular process does sailcloth for paragliding undergo? | |||
| 1 | Surface coating with silicon and polyurethane for better protection against general wear and to UV exposure | ||
| -1 | Stretching of the fabric | ||
| -1 | Heat shrinkage of the fabric | ||
| -1 | Surface treatment with water repellent coating | ||
| E025 | 1 | E | S |
| What is the name of the instrument used to measure air humidity | |||
| 1 | Hygrometer | ||
| -1 | Anemometer | ||
| -1 | Thermometer | ||
| -1 | Variometer | ||
| -1 | Speed Probe | ||
| E026 | 1 | E | S |
| For a given wing what are the consequences of a reduction in the load on the wing? | |||
| 1 | If one stays within the specified weight range by the manufacturer, all the flight speeds and sink rate decrease in the same proportion. | ||
| 1 | If one is below the recommended minimum weight the wing may have less resistance to turbulence and may tend to collapse more easily | ||
| -1 | If one stays within the specified weight range by the manufacturer, all the flight speeds and sink rate will stay the same | ||
| -1 | If one is below the recommended minimum weight the wing will have a higher sink rate | ||
| E027 | 1 | E | S |
| How much lift is generated by the top surface of a wing | |||
| 1 | around two thirds of the lift is generated by the top of a wing | ||
| -1 | lift is evenly distributed over a wing surface, half half | ||
| -1 | most lift is generated by the bottom surface of a wing, the top hardly contributes to any lift | ||
| -1 | one third of the lift is generated by the top surface of a wing | ||
| E028 | 1 | E | S |
| Which types of drag has a Paraglider got ... | |||
| 40 | Induced Drag = caused by the bound vortex around the profile | ||
| 30 | Profile Drag = caused by friction | ||
| 30 | Form Drag = caused by the pilot and the lines | ||
| -1 | Harness Drag = Pilot + Harness | ||
| E029 | 1 | E | S |
| a pilot with all up weight of 100 kg flies at a best glide of 40 km/h. If he adds 10 kg of ballast , how much will his best glide speed increase? | |||
| 1 | By approximately 2 km/h to 42 km/h | ||
| -1 | The best glide speed is not influenced by the all up weight | ||
| -1 | By approximately 5 km/h to 45 km/h | ||
| -1 | By approximately 10 km/h to 50 km/h | ||
| E030 | 1 | E | S |
| Glide ratio is defined in still air as ... | |||
| 1 | Horizontal velocity / vertical velocity | ||
| 1 | Horizontal distance travelled / Vertical distance travelled | ||
| 1 | Lift / Drag | ||
| -1 | Maximum Speed / Best Glide Speed | ||
| -1 | Maximum Speed / Minimum Speed | ||
| -1 | Trim Speed / Best Glide Speed | ||
| -1 | Minimum Sink / Maximum Sink | ||
| E031 | 1 | E | S |
| Your glide ratio gets influenced by ... | |||
| 1 | The wind speed and direction that you are flying | ||
| 1 | How much brake you apply on your wing | ||
| 1 | applying speed bar | ||
| -3 | flying with ballast or not | ||
| E032 | 1 | E | S |
| Where can one expect to have Kevlar lines break ? | |||
| 1 | End of the stitching above the maillons, where they bend most when you launch | ||
| -1 | at the loop where they connect to the glider | ||
| -1 | at the loop where they connect with other lines | ||
| -1 | where they touch the metal | ||
| E033 | 1 | E | S |
| Maillon is ... ? | |||
| 1 | a small metal screw carabiner that connects the lines with the riser | ||
| -1 | the little loop in the canopy to connect the lines | ||
| -1 | the type of knot used to secure the toggle to the toggle line | ||
| -1 | the device to adjust the straps in your harness | ||
| -1 | a Paraglider cloth material | ||
| -1 | a Paraglider line material | ||
| E034 | 1 | E | B |
| The Speedbar accellerator system gets connected to ... | |||
| 1 | the riser system | ||
| -1 | brake line | ||
| -1 | break line | ||
| -1 | the toggles | ||
| E035 | 1 | E | B |
| A pully is ... | |||
| 1 | to guide the speedsystem in the harness | ||
| -1 | the pin that is part of your winch tow release | ||
| -1 | is a pin used in your reserve deployment bag | ||
| -1 | connected to your steering line and you put your hand in it | ||
| E036 | 1 | E | B |
| Drag ... | |||
| 1 | is pointing in the opposite direction of your airspeed | ||
| -1 | is pointing upwards from your flying direction | ||
| -1 | is pointing forwards in the direction of your flight | ||
| -1 | is pointing downwards to the ground | ||
| E037 | 1 | E | B |
| Lift ... | |||
| 1 | gets generated by the shape of the airfoil | ||
| 1 | gets created by air flowing over and below the airfoil | ||
| -1 | gets created by the cells in a paraglider having a lower air density | ||
| -1 | gets created by a lower pressure on the bottom surface and higher pressure on the top surface of a wing | ||
| 1 | gets created by a lower pressure on the top surface and higher pressure on the bottom surface of a wing | ||
| E038 | 1 | E | B |
| Running faster on takeoff ... | |||
| 1 | will create more lift | ||
| -1 | will make the canopy more prone to collapse | ||
| -1 | will put the wing closer to stall point | ||
| -1 | will make the canopy less responsive to toggle input | ||
| E039 | 1 | E | B |
| What does this picture show ... | |||
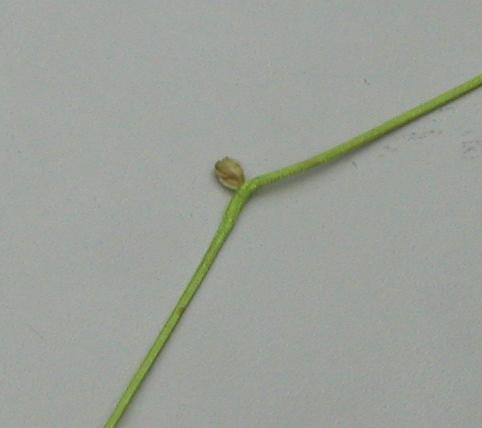 |
|||
| 1 | A Paraglider line which needs to be replaced | ||
| -1 | A track log going past a turnpoint | ||
| -1 | A winch release | ||
| -1 | A dihedral aerial for a 2m band radio | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/deutsch/news/index.html | |||
| E040 | 1 | E | B |
| What does this picture show ... | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A Paraglider line which needs to be replaced | ||
| -1 | A track log going over a turnpoint | ||
| -1 | The famous green flash sunset seen from Signal Hill | ||
| -1 | The famous green flash sunset never seen from Porterville's Flyers Lodge | ||
| -1 | What the world looks like when you get hypoxic at extreme high altitude | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/deutsch/news/index.html | |||
| E041 | 1 | E | B |
| What is A in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Lift | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Gravity | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| -1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| -1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E042 | 1 | E | B |
| What is B in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Lift | ||
| 1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Gravity | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| -1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| -1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E043 | 1 | E | B |
| What is C in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Lift | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| 1 | Gravity | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| -1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| -1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E044 | 1 | E | B |
| What is D in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Lift | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Gravity | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| 1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| -1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E045 | 1 | E | B |
| What is E in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Lift | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Gravity | ||
| 1 | Chord | ||
| -1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| -1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E046 | 1 | E | B |
| What is F in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Lift | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Gravity | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| -1 | Angle of Attack | ||
| 1 | Relative Airflow | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E047 | 1 | E | B |
| What is A in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Low Pressure | ||
| -1 | High Pressure | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E048 | 1 | E | B |
| What is B in this picture | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Low Pressure | ||
| 1 | High Pressure | ||
| -1 | Drag | ||
| -1 | Chord | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/hammer/loresivm.htm | |||
| E049 | 1 | E | B |
| What does this picture demonstrate | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Why one should not fly above cloud | ||
| 1 | It shows the Vortex of a wing | ||
| -1 | Why one should stay below ceiling | ||
| -1 | Katabatic airflow of the mountain range in the background | ||
| 1 | It shows the downdraft behind a wing | ||
| http://nasaexplores.com/lessons/02-025/k-4_2-t.html | |||
| E050 | 1 | E | B |
| Wearing gloves | |||
| 1 | Is a good idea in Paragliding | ||
| 1 | Will come handy when you have to abort or getting dragged | ||
| 1 | Helps when you have to tuck ears | ||
| 1 | Comes handy when your glider is in a thorn tree | ||
| -2 | Is only required to wear in winter | ||
| -2 | Is only required for DHV 2 or higher rated gliders | ||
| E051 | 1 | E | S |
| Making the cell openings at the leading edge smaller | |||
| 1 | Will give the glider a better glide performance | ||
| 1 | Will make the glider faster | ||
| 1 | Will make the glider more difficult to inflate | ||
| 1 | Will make the glider more prone to collapses | ||
| -2 | Will make the glider more stable | ||
| -2 | Will make the glider slower | ||
| E052 | 1 | E | S |
| When pulling up your glider , your canopy tends to hang back and not come forward completely | |||
| 1 | Check your lines for shrinkage | ||
| 1 | Danger of parachutal stall tendency | ||
| -1 | Something wrong with your speedbar | ||
| -1 | Rocks in the trailing edge | ||
| E053 | 1 | E | S |
| You can receive on your 2m radio but they can not hear you | |||
| 1 | Your battery is probably going flat | ||
| -1 | The TX is not switched on | ||
| -1 | Aerial is not connected | ||
| -1 | The other party has not switched on the RX option | ||
| E054 | 1 | E | B |
| What is a streamer | |||
| 1 | A stripe of cloth that one attaches to a stick to indicate the wind direction | ||
| -1 | A bite nippletube that provides you with a stream of water to drink while flying | ||
| -1 | A speedprobe that hangs in your slip stream to measure your air speed | ||
| -1 | A tight fitting flight suit to give you best aerodynamics | ||
| E055 | 1 | E | S |
| Your Camelbag shows signs of weird stuff growing in it | |||
| 1 | Use Milton and live with the after taste | ||
| -1 | Throw it away, it has had it | ||
| -1 | Boil it in hot water for half an hour | ||
| -1 | Fill with some strong alcohol to desinfect it | ||
| E056 | 1 | E | B |
| You just landed and a black gust front is catching up with you | |||
| 1 | Protect your glider from getting wet | ||
| -1 | Wrap yourself into your glider to avoid getting wet and keep warm | ||
| -1 | Disconnect the glider from the harness and keep the harness on | ||
| -1 | Inflate the canopy and use the extra pull to help you walk faster | ||
| E057 | 1 | E | S |
| You want to use your GPS to locate a lost thermal while in flight | |||
| 1 | Use a 1 or 2 seconds track sample interval | ||
| -1 | Use a 15 seconds track interval | ||
| 1 | Use a zoom area of around 500 meters | ||
| -1 | Use a zomm area of around 5 km | ||
| -1 | Use FILL Mode | ||
| 1 | Use WRAP Mode | ||
| 1 | Expect to run out of memory for a complete tracklog of your flight | ||
| E058 | 1 | E | B |
| Split A risers .... | |||
| 1 | means you got 2 A risers on each side | ||
| -1 | is a serious damage to the Paraglider | ||
| 1 | helps when tucking ears | ||
| 1 | might only require the inner ones to be used for inflating the canopy | ||
| -1 | means that you need cross braces on the harness | ||
| -1 | means that you need a speedbar to make use of them | ||
| E059 | 1 | E | B |
| The lines are connected to the risers by | |||
| 1 | Maillons | ||
| -1 | Carabiners | ||
| -1 | Double sleeved knots | ||
| -1 | the speedbar | ||
| E060 | 1 | E | B |
| What is the metal piece in that picture called ? | |||
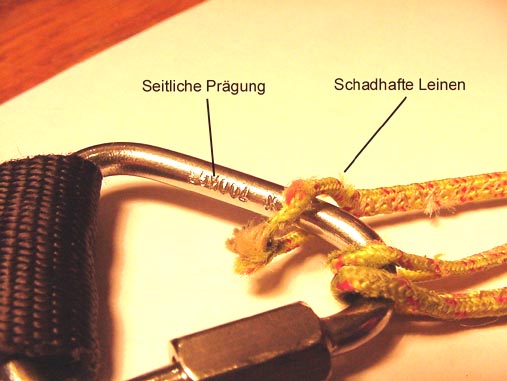 |
|||
| 1 | Maillon | ||
| -1 | Carabiner | ||
| -1 | Speedbar | ||
| -1 | Quick Release | ||
| E061 | 1 | E | B |
| A Carabiner connects | |||
| 1 | the harness with the risers | ||
| -1 | the lines with the risers | ||
| -1 | the speedprobe with the vario | ||
| -1 | the GPS with the vario | ||
| E062 | 1 | E | B |
| A good back protection ... | |||
| -1 | has a high G load test value | ||
| 1 | has a low G load test value | ||
| -1 | is heavy | ||
| 1 | is light | ||
| 1 | is small to pack | ||
| -1 | is bulky to pack | ||
| E063 | 1 | E | B |
| Front mounted reserves | |||
| 1 | can be used with any of your hands to be deployed | ||
| -1 | can only be used with the left hand to be deployed | ||
| -1 | can only be used with the right hand to be deployed | ||
| -1 | are not recommended | ||
| E064 | 1 | E | B |
| To deploy your reserve ... | |||
| 1 | decide - throw into a clear area - ..... - bring in your glider | ||
| -1 | undo your chect strap - find handle - throw above you | ||
| -1 | put glider into full stall to have canopy fall behind you to get a clear area to throw your reserve | ||
| -1 | fill out the incident report first then throw your reserve | ||
| -1 | get permission from the LSO or NSTO first | ||
| -1 | collapse your glider - find handle - pull and throw against spin direction | ||
| E065 | 1 | E | B |
| Suitable Backprotectors to reduce the impact are | |||
| 1 | Airbag | ||
| 1 | Foam cushion | ||
| -1 | Kevlar backplates | ||
| -1 | plywood backplates | ||
| -1 | a big backpack | ||
| E066 | 1 | E | B |
| A stuff bag | |||
| 1 | is a container for your paraglider | ||
| -1 | is a container for your reserve | ||
| -1 | is a backprotection | ||
| -1 | is used to hold your helmet and other goodies | ||
| E067 | 1 | E | B |
| The recommended way to pack a Paraglider is | |||
| 1 | by rolling it up from the tips towards the centerr | ||
| 1 | by concertinaing it from the center towards the tips | ||
| 1 | by moving the outer tip towards the center and repeating this | ||
| -1 | by rolling the trailing edge towards the leading edge | ||
| -1 | by bunching it up and stuffing it into the stuff bag | ||
| E068 | 1 | E | B |
| The suns UV rays | |||
| 1 | damage your canopy over time | ||
| -1 | generate the thermals | ||
| -1 | cause the clouds to look white | ||
| -1 | will give your glider a brown tan over time | ||
| 1 | are stronger in the Highveld compared to the coast | ||
| -1 | are stronger at the coast compared to the Highveld | ||
| E069 | 1 | E | B |
| A Paraglider canopy material | |||
| 1 | is coated to reduce porosity | ||
| -1 | is coated to improve porosity | ||
| -1 | has to be porous to be a good wing | ||
| 1 | has to have a low porosity to be a good wing | ||
| E070 | 1 | S | B |
| Porosity is measured in | |||
| 1 | seconds | ||
| -1 | meters per second | ||
| -1 | hectoPascal | ||
| -1 | Newton per square centimeter | ||
| E071 | 1 | S | B |
| You can check the prosity of a wing | |||
| 1 | by sucking on your canopy | ||
| 1 | by applying a porosity meter | ||
| -1 | by pushing your thumb on the material | ||
| -1 | by stress testing the fabric | ||
| E072 | 1 | E | B |
| The thumb test is | |||
| 1 | pressing your thumb on the fabric of your canopy and see if it breaks | ||
| -1 | is another expression for the 5 point checks - thumbs up | ||
| -1 | used to check porosity | ||
| -1 | used to check the glide angle, can you make it to landing | ||
| E073 | 1 | E | S |
| To check a canopy for airworthiness | |||
| 1 | do a porosity check | ||
| 1 | do a thumbtest | ||
| 1 | check for line stretch or shrinkage | ||
| 1 | check for any damage | ||
| 1 | do a fabric stress test by hand pulling on some cells | ||
| -1 | do a resonance frequency test of the wing | ||
| -1 | fly the wing at maximum speed and look for flutter | ||
| -1 | inspect the ribs with a boroscope | ||
| E074 | 1 | E | S |
| The Bernoulli equation is used | |||
| 1 | to explain the lift around a wing shape | ||
| -1 | to calculate the thermal strength | ||
| -1 | to calculate the cloudbase | ||
| -1 | to calculate the great circle distance | ||
| E075 | 1 | E | S |
| Airpressure | |||
| 1 | drops by 1 mb or 1 hPa for 10 meters up | ||
| -1 | drops by 1 mb or 1 hPa for 10 meters down | ||
| -1 | stays constant | ||
| -1 | drops by 1 degree per 100 meters higher up | ||
| E076 | 1 | E | S |
| Which axis definitions are correct | |||
| 1 | Yaw - Normal axis | ||
| 1 | Roll - Longitudinal axis | ||
| 1 | Pitch - Lateral axis | ||
| -1 | Pitch - Normal axis | ||
| -1 | Yaw - Longitudinal axis | ||
| -1 | Roll - Lateral axis | ||
| -1 | Roll - Normal axis | ||
| -1 | Pitch - Longitudinal axis | ||
| -1 | Yaw - Lateral axis | ||
| E077 | 1 | E | S |
| Which forces counter each other in a Paraglider | |||
| 1 | Lift and Drag combined versus the Weight | ||
| -1 | Thrust versus Drag | ||
| -1 | Lift versus Weight | ||
| -1 | Weight versus Drag | ||
| E078 | 1 | E | S |
| A Paraglider with longer lines | |||
| 1 | tends to have more pitch pendulum | ||
| -1 | tends to have less pitch pendulum | ||
| 1 | will have more drag | ||
| -1 | will have less drag | ||
| 1 | can have a straighter, better wing | ||
| E079 | 1 | E | B |
| A compression strap | |||
| 1 | is used when folding up and packing your glider | ||
| 1 | is part of your reserve deployment | ||
| -1 | is connected by a buckle to your chest strap | ||
| -1 | is part of your harness | ||
| E080 | 1 | E | S |
| Using fat and grease in your oxygen system | |||
| 1 | is extremely dangerous | ||
| -1 | is advisable to advoid any clogging up of your airflow | ||
| -1 | is required to avoid freezing up of your kit | ||
| -1 | will enable you to dismantle it after getting to freezing level | ||
| E081 | 1 | E | S |
| To refill your oxygen bottle use .. | |||
| 1 | only dried oxygen, like it gets used in hospitals | ||
| -1 | any oxygen bottle, as it is used for welding will do | ||
| -1 | use a scuba diving tank to refill it | ||
| -1 | use any garage air pressure pump to refill | ||
| E082 | 1 | E | B |
| A glide ratio of 7 means ... | |||
| 1 | for every meter down in calm air one gets 7 meters forward | ||
| -1 | one glides down on a 7 dgree angle | ||
| -1 | best glide at 7 percent of brake | ||
| -1 | one has to fly 7 m/s or about 26 km/h for best glide | ||
| E083 | 1 | E | B |
| What will happen when you clip in your risers twisted | |||
| 1 | The brakes will be sticky to control | ||
| -1 | The brakes will be completely unusable | ||
| -1 | You will not manage to inflate the canopy | ||
| -1 | Nothing | ||
| E084 | 1 | E | S |
| What is A | |||
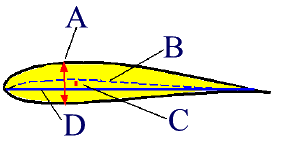 |
|||
| 1 | Thickness | ||
| -1 | Mean Camber Line | ||
| -1 | Camber | ||
| -1 | Chord Line | ||
| E085 | 1 | E | S |
| What is B | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Thickness | ||
| 1 | Mean Camber Line | ||
| -1 | Camber | ||
| -1 | Chord Line | ||
| E086 | 1 | E | S |
| What is C | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Thickness | ||
| -1 | Mean Camber Line | ||
| 1 | Camber | ||
| -1 | Chord Line | ||
| E087 | 1 | E | S |
| What is D | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Thickness | ||
| -1 | Mean Camber Line | ||
| -1 | Camber | ||
| 1 | Chord Line | ||
| E088 | 1 | E | S |
| All new hang gliders and paragliders sold in South Africa | |||
| 1 | shall have been certified by an approved test Authority and carry a label with the manufacturers name, a serial number, date of manufacture, quality controller's signature, pilot mass range and the class rating | ||
| 1 | shall be classified in the Glider Classification Schedule | ||
| -1 | must have a red left wingtip and a green right wing tip | ||
| -1 | must be testflown first by a local test pilot | ||
| SAHPA Ops and Proc and CAA CATS and CARS | |||
| E089 | 1 | E | B |
| What is this? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Carabiner | ||
| -1 | Speedbar | ||
| -1 | Riser | ||
| -1 | Harness | ||
| http://www.gleitschirm-magazin.com/pdf/karabinerkaputt.pdf | |||
| E090 | 1 | E | B |
| This picture shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | An Old Paraglider design from the early days | ||
| -1 | A high performance canopy | ||
| -1 | A Hang Glider | ||
| -1 | A reserve parachute | ||
| http://www.gleitschirm-magazin.com/pdf/konzeption2.pdf | |||
| E091 | 1 | E | B |
| Your reserve deployment can be delayed by | |||
| 1 | too much velcro making the handle stick too hard | ||
| 1 | the inflated airbag pressing against the side or back mounted reserve | ||
| -1 | the current airpressure pushing against the deployment bag | ||
| 1 | how easy you can find and reach the handle | ||
| E092 | 1 | E | B |
| A front mounted reserve | |||
| 1 | is easy to find when one has to deploy it | ||
| 1 | can be used as a cockpit for your instruments | ||
| -1 | is the worst place to have your reserve located | ||
| -1 | can not be deployed | ||
| E093 | 1 | E | B |
| Trim Tabs | |||
| 1 | are part of the risers | ||
| -1 | are part of the speed bar | ||
| -1 | are part of the harness | ||
| -1 | make your harness more sensitive | ||
| E094 | 1 | E | B |
| Trim Tabs | |||
| 1 | can change the behaviour and response and rating of a wing | ||
| -1 | do not influence the behaviour of a wing | ||
| -1 | modify the aspect ration of a wing | ||
| -1 | do not change the angle of attack | ||
| E095 | 1 | E | B |
| Trim Tabs | |||
| 1 | change the angle of attack of a wing | ||
| -1 | do not influence the behaviour of a wing | ||
| -1 | modify the aspect ration of a wing | ||
| -1 | do not change the angle of attack | ||
| E096 | 1 | E | B |
| Trim Tabs | |||
| 1 | make a wing slower or faster | ||
| -1 | do not influence the behaviour of a wing | ||
| -1 | modify the aspect ration of a wing | ||
| -1 | do not change the angle of attack | ||
| E097 | 1 | E | B |
| With higher altitude your | |||
| 1 | can carry less load | ||
| -1 | can carry more load | ||
| 1 | wing will fly faster | ||
| -1 | wing will fly slower | ||
| E098 | 1 | E | B |
| Which is a pressure based instrument | |||
| 1 | Vario | ||
| -1 | GPS | ||
| -1 | cell phone | ||
| -1 | Radio transceiver | ||
| E099 | 1 | E | B |
| A Vario | |||
| 1 | is airpressure based | ||
| -1 | works off satellite signals | ||
| -1 | is radar based | ||
| -1 | is ultrasound based | ||
| E100 | 1 | E | S |
| Velcro used with a reserve parachute | |||
| 1 | can damage the lines and fabric by abrasion | ||
| 1 | can stick together and make it hard to open if not deployed every 3 months | ||
| -1 | is a must | ||
| -1 | is not allowed | ||
| E101 | 1 | E | S |
| Same make of the wing, the larger wing | |||
| 1 | will have a better glide compared to the smaller wing of the same model | ||
| -1 | will have a worse glide compared to the smaller wing of the same make | ||
| -1 | will have the same performance characteristics as the other sizes | ||
| -1 | will usually react more violent and faster to any disturbance | ||
| XC Mag October 2003 Bruce Goldsmith | |||
| E102 | 1 | E | B |
| Porosity of your canopy | |||
| 1 | can cause your wing to go Parachutal | ||
| -1 | is necessary to avoid wing stalls | ||
| -1 | is only a problem when flying in rain | ||
| -1 | will improve the handling of your paraglider | ||
| E103 | 1 | E | B |
| Line shrinkage | |||
| 1 | can cause your wing to go Parachutal | ||
| -1 | is necessary to avoid wing stalls | ||
| -1 | is only a problem when flying in rain | ||
| -1 | will improve the handling of your paraglider | ||
| E104 | 1 | E | S |
| What is this used for? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A winching support which makes winch launches easier for the pilot | ||
| -1 | a reserve bridle | ||
| -1 | attachment for a reserve | ||
| -1 | stirrup | ||
| http://www.dhv.de | |||
| E105 | 1 | E | B |
| What is a stirrup? | |||
| 1 | A foot rest attched to the harness which helps the pilot get into the seat after takeoff | ||
| -1 | an accellerator system attached to the A risers | ||
| -1 | attachment for a reserve to make it longer | ||
| -1 | a winch support which helps avoiding parachutal stalls | ||
| whatever | |||
| E106 | 1 | E | B |
| What type of footwear should be used for Paragliding? | |||
| 1 | boots with ankle support | ||
| -1 | running shoes | ||
| -1 | comfortable takkies | ||
| -1 | slip slops or barefoot is best | ||
| lots of broken ankles | |||
| E107 | 1 | E | S |
| Changing the width of your harness chest strap | |||
| 1 | can influence the CEN or DHV glider rating | ||
| -1 | does not make a difference on how a glider will react in turbulence | ||
| -1 | is not possible | ||
| -1 | is only required when you fly tandem | ||
| Skywing 12 2003 | |||
| E108 | 1 | E | S |
| To avoid line twisting when having a wing deflation | |||
| 1 | sitting upright will reduce the risk | ||
| -1 | flying supine will reduce the risk | ||
| -1 | a spreaderbar will reduce the risk | ||
| -1 | a speedbar will reduce the risk | ||
| Skywing 12 2003 | |||
| E109 | 1 | E | S |
| What can cause a Paraglider to go parachutal | |||
| 1 | wing becoming porous | ||
| 1 | flying a wet canopy, or in rain | ||
| 1 | inproper exit out of a B-Line stall | ||
| 1 | not having the canopy properly above the pilot on a winch launch | ||
| 1 | line shrinkage | ||
| 1 | applying too much speedbar | ||
| E110 | 1 | E | S |
| What are the pro's and cons of comp lines | |||
| 1 | thin lines on competition gliders, less drag | ||
| 1 | have less strength | ||
| 1 | need replacement more often | ||
| 1 | are stronger | ||
| E111 | 1 | E | B |
| For a reverse winch launch one has to get the winch line from .. | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | From the right | ||
| -1 | From the left | ||
| -1 | Does not matter, any side will do | ||
| -1 | One can not winch with a reverse launch | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Verkehrt_ausgedreht.1697.0.html | |||
| E112 | 1 | E | B |
| For a reverse winch launch one has to get the winch line from .. | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | From the right | ||
| 1 | From the left | ||
| -1 | Does not matter, any side will do | ||
| -1 | One can not winch with a reverse launch | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Verkehrt_ausgedreht.1697.0.html | |||
| E113 | 1 | E | B |
| Comparing 2 Gliders. Both got the same size. Glider A has more cells. Glider A ... | |||
| 1 | should have better performance | ||
| 1 | be heavier | ||
| 1 | cost more | ||
| -1 | have a higher all up weight range | ||
| E114 | 1 | E | B |
| This picture shows ... | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | what can happen when you land on a busy road | ||
| -1 | a Microlight | ||
| -1 | when aircrafts and land vehicles collide on take off | ||
| 1 | a PPG stunt | ||
| E115 | 1 | E | B |
| A reserve has a 6m/s sinkrate at sea level specification for 90kg all up. You take off from a 1600m ASL site. Your sink rate will be ... | |||
| 1 | higher | ||
| -1 | lower | ||
| -1 | the same | ||
| 1 | higher if you are heavier than 90kg all up | ||
| E116 | 1 | E | B |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Vortex of a wing | ||
| -1 | rotor on a wing | ||
| -1 | katabtic airflow around a wing | ||
| -1 | anabatic airflow around a wing | ||
| http://www.skywalk.info | |||
| E117 | 1 | E | S |
| On a payout winch the tension was set too high | |||
| 1 | as a winch driver drive faster to pay out the line | ||
| -1 | drive slower to pay out more line | ||
| -1 | drive as usual | ||
| -1 | the pilot must release | ||
| E118 | 1 | E | S |
| Rule of thumb for setting tension on a payout winch | |||
| 1 | half the amount of the all up weight of the pilot | ||
| -1 | about the same as the all up weight of the pilot | ||
| -1 | use abut 1/10 of the all up weight of the pilot | ||
| -1 | keep it fixed to the factory setting | ||
| E119 | 1 | E | B |
| For an SIV over water | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | fly with a floating vest | ||
| 1 | remove any airbag | ||
| 1 | remove any foam back protection | ||
| -1 | one has to dress like this DHV test pilot | ||
| E120 | 1 | E | B |
| A stuffbag is used | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | for packing your glider away | ||
| -1 | in packing your reserve | ||
| -1 | is required for a SIV course | ||
| -1 | as a back protection | ||
| E121 | 1 | E | B |
| This picture shows a | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | tow assist | ||
| -1 | racing speed system | ||
| 1 | which avoids parachutals on launch | ||
| -1 | prevents frontal collapses | ||
| E122 | 1 | E | B |
| A rescue line is used for | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | in a tree landing to pull up another rope | ||
| -1 | in a tree landing to support your weight when climbing down | ||
| -1 | for fishing | ||
| -1 | measuring the water depth before crossing a river | ||