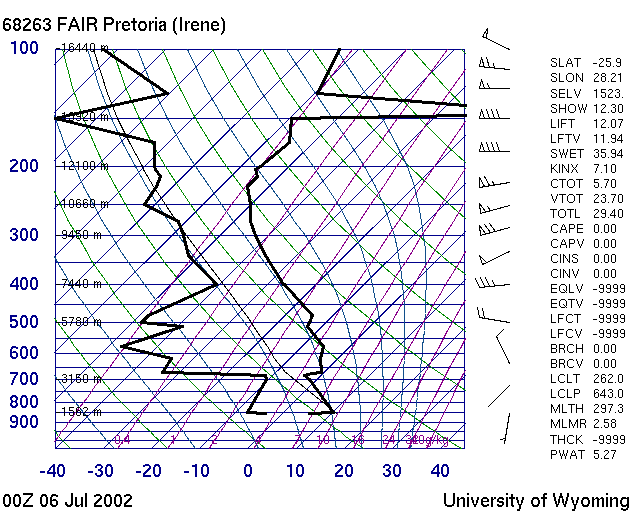
| M001 | 1 | M | S |
| What would be the Trigger temperature for this day? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | 10 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | 20 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | 0 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | 30 Degree Celsius | ||
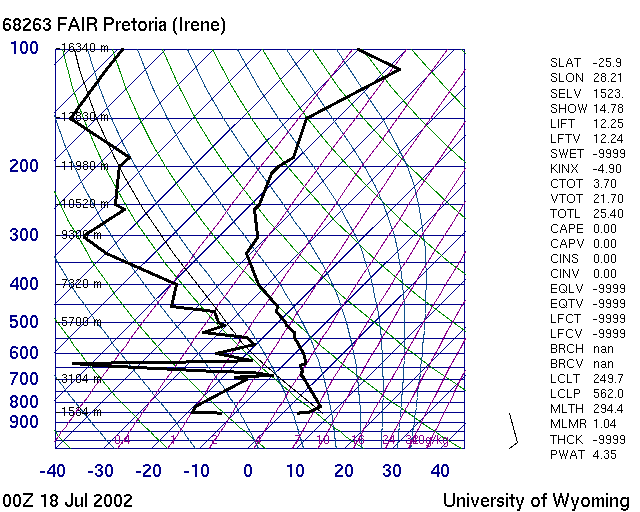
| M002 | 2 | M | S |
| What does this picture show... ? | |||
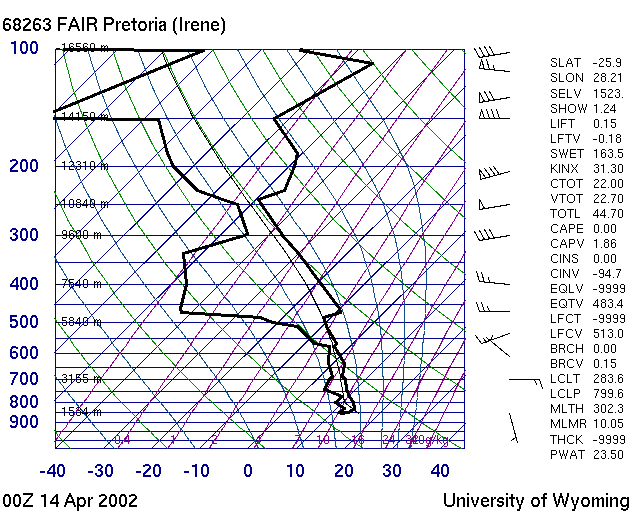 |
|||
| -1 | A Track log | ||
| 1 | A humid day Skew T Diagram | ||
| -1 | A Paraglider Polare | ||
| -1 | A good day T Phi Diagram | ||
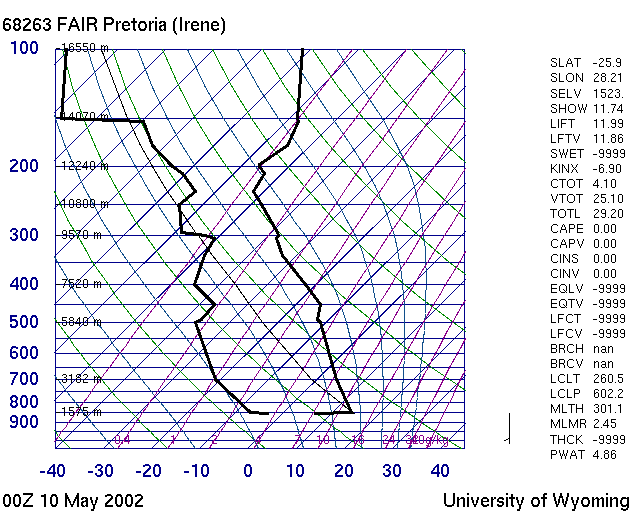
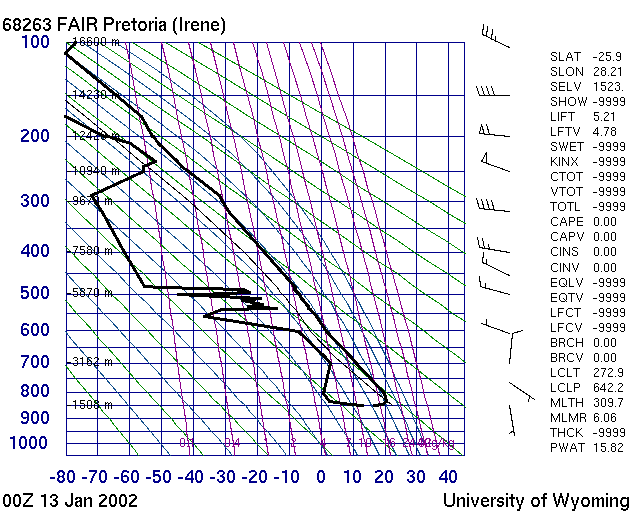
| M003 | 3 | M | S |
| Which of these pictures show a good day ? | |||
| -1 | 10 May 2002 | ||
 |
|||
| 1 | 13 Jan 2002 | ||
 |
|||
| -1 | 14 April 2002 | ||
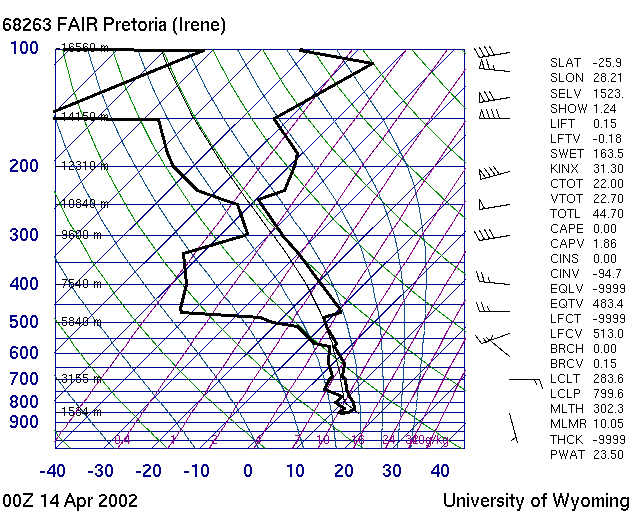 |
|||
| -1 | 25 May 2002 | ||
 |
|||
| M004 | 1 | M | S |
| Wind | |||
| 1 | tends to flow from High Pressure to Low pressure | ||
| -1 | tends to flow from Low Pressure to High Pressure | ||
| -1 | has nothing to do with Highs and Lows | ||
| -1 | can flow from High to Low and the other way | ||
| M005 | 1 | M | S |
| A High pressure system tends to turn the wind | |||
| 1 | clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere | ||
| 1 | counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere | ||
| -1 | clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere | ||
| -1 | counter clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere | ||
| M006 | 1 | M | S |
| Wind in the Highveld tends to | |||
| 1 | swing counter clockwise during the day | ||
| -1 | swing clock wise during the day | ||
| 1 | get influenced by Coriolis force during the day | ||
| -1 | become katabatic at noon | ||
| M007 | 1 | M | S |
| The Met office is giving you a wind of 270 and 20 knots on the ground | |||
| 1 | The wind is blowing from a Westerly direction | ||
| -1 | 20 knots is ok to fly a Paraglider on a ridge | ||
| 1 | 20 knots is too strong to fly a Paraglider | ||
| -1 | The wind will be Easterly | ||
| M008 | 1 | M | S |
| Graaf Reinet, Valley of Desolation,a cold front is approaching from Cape Town .Expect.. | |||
| -1 | good flying, Bergwind conditions | ||
| -1 | Blown out, rough , gusty, Bergwind blowing from the coast | ||
| 1 | Blown out, rough, gusty, Bergwind blowing from the Karoo | ||
| -1 | Smooth ridge soaring sea breeze | ||
| M009 | 1 | M | S |
| September or October in the Highveld. No rain yet, what thermic conditions can be expected? | |||
| 1 | Gusty, punchy thermic conditions | ||
| -1 | Strong inversions and weak thermals | ||
| -1 | Lots of thunderstorms | ||
| -1 | Smooth ridge soaring conditions | ||
| M010 | 1 | M | S |
| You took off from Dasklip. And you are now flying up the Olifantsvalley near the Cedarberg with the wind from the back. At a place called Constriction the valley gets narrower. What conditions can you expect? | |||
| 1 | Lift due to convergence | ||
| 1 | Strong wind from the back, landing in strong wind. Turbulence near the ground | ||
| -1 | An inversion layer will build up, killing the thermals | ||
| -1 | Thunderstorms due to the air getting squeezed into wet adiabatic conditions | ||
| M011 | 1 | M | B |
| Thunderstorms can | |||
| 1 | be dangerous , stay away from them | ||
| -1 | An indication of good lift. So try get under them and gain height | ||
| 1 | create gust fronts which make it very difficult to land in a controlled way | ||
| -1 | break inversion layers to allow thermals to start working | ||
| M012 | 1 | M | S |
| The trough axis | |||
| 1 | is a boundary between humid subtropical air and dry desert air | ||
| -1 | a boundary between seabreeze and bergwind | ||
| 1 | provides good x-country flying in summer | ||
| -1 | is located in winter over Mpumalanga and creates good flying | ||
| M013 | 1 | M | S |
| Lenticularis clouds indicate | |||
| -1 | Good lift underneath them | ||
| 1 | Strong winds | ||
| -1 | A gust front is approaching | ||
| -1 | A cold front has passed through | ||
| M014 | 1 | M | S |
| Isobars close together on a synoptic chart indicate | |||
| 1 | Strong wind | ||
| -1 | An altitude terrain change, like a slope or a hill | ||
| -1 | A temperature change, like a cold front is passing through | ||
| -1 | A change in the magnetic field, caused by iron ore in the ground | ||
| M015 | 1 | M | S |
| A squall line | |||
| 1 | indicates the wind will pick up soon | ||
| -1 | indicates the wind will drop soon | ||
| 1 | is similar to a gust front but coastal coming from the sea | ||
| -1 | is an expression used in a competition for a line that can only be crossed once the window is open | ||
| M016 | 3 | M | S |
| While flying cross-country you notice a Nimbocumulus build up in front of you. You also notice below it that the visibility at the horizon is poor. What is a Nimbocumulus? What is causing the poor visibility and what is your plan of action? | |||
| 1 | A thunderstorm cloud indicating a gust front and you better land fast | ||
| -1 | A wave cloud , good lift, get there quickly | ||
| -1 | A convergence cloud, expect steady smooth lift | ||
| -1 | A cloud that will rain soon, stay high and fly around it | ||
| M017 | 1 | M | S |
| What height of cloud base AGL can be expected when the dew point is 15 degree Celsius and the expected maximum temperature is 30 degree Celsius. | |||
| 1 | Around 1500 meters | ||
| -1 | Around 1000 meters | ||
| -1 | Around 2000 meters | ||
| -1 | can not be determined | ||
| M018 | 1 | M | S |
| Convergence lift | |||
| 1 | occurs when 2 airmasses come together and create lift | ||
| -1 | can be found behind a hill in the lee | ||
| -1 | when a cloud goes very dark and starts growing higher | ||
| -1 | can be found downwind from an obstacle in stable conditions | ||
| M019 | 1 | M | S |
| By how much does an air particle cool down as it rises 100m without its water content condensing | |||
| 1 | 1 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | 0.5 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | It does not cool down, it warms up by 1 Degree Celsius | ||
| -1 | It does not cool down, it warms up by 0.5 Degree Celsius | ||
| M020 | 1 | M | S |
| What is a trough | |||
| 1 | A line of low pressure in the atmosphere | ||
| 1 | A U shaped anticyclone where the air flows clockwise around in South Africa | ||
| -1 | a High pressure | ||
| -1 | An expression for a coastal low created by an approaching cold front | ||
| M021 | 1 | M | S |
| In the Southern Hemisphere, which way do depressions rotate? | |||
| 1 | Clockwise | ||
| -1 | Anticlockwise | ||
| -1 | Depends which way the cold front that creates them is moving | ||
| -1 | In summer clockwise, in winter counterclockwise | ||
| M022 | 1 | M | S |
| In the Northern Hemisphere, which way do depressions rotate? | |||
| -1 | Clockwise | ||
| 1 | Anticlockwise | ||
| -1 | Depends which way the cold front that creates them is moving | ||
| -1 | In summer clockwise, in winter counterclockwise | ||
| M023 | 1 | M | S |
| What is the breathable layer of the atmosphere called ? | |||
| 1 | Troposphere | ||
| -1 | Mesosphere | ||
| -1 | Stratosphere | ||
| -1 | Tropopause | ||
| M024 | 1 | M | B |
| Thunderstorm is approaching. The thunder can be heard 10 seconds after the lightning | |||
| 1 | The flash was 3 km away | ||
| -1 | The flash was 30 km away | ||
| -1 | The flash was 10 km away | ||
| -1 | The flash was 1 km away | ||
| M025 | 1 | M | S |
| Which meteors originate from atmospheric water? | |||
| 1 | rain | ||
| 1 | hail | ||
| 1 | cloud | ||
| 1 | snow | ||
| -4 | comets | ||
| M026 | 1 | M | S |
| What is the domain between the troposphere and stratosphere called? | |||
| 1 | Tropopause | ||
| -1 | Stratopause | ||
| -1 | Mesopause | ||
| -1 | Menopause | ||
| M027 | 1 | M | S |
| A balloon sounding done 00Z in Pretoria with an Easterly wind of 5 knots | |||
| 1 | Will be relevant 14.00 local time 120 km to the West of Pretoria | ||
| -1 | will be relevant 12.00 local time and 120 km to the west of Pretoria | ||
| -1 | will be relevant 10.00 local time and 120 km to the west of Pretoria | ||
| -1 | will be relevant 12.00 local time and 60 km to the west of Pretoria | ||
| M028 | 1 | M | S |
| A thick, gray, dense cloud from 3000 - 5000 meters altitude, with no contrast on its base, covering a large part of the sky | |||
| 1 | is called a Nimbostratus | ||
| -1 | is a Cirrus | ||
| -1 | is a Lenticularis | ||
| -1 | is a Altocumulus Castellanus | ||
| M029 | 1 | M | S |
| An Altocumulus Castelanus | |||
| 1 | is an early indication for thunderstorms in a few hours | ||
| -1 | indicates wave lift under it | ||
| -1 | indicates a warm front approaching | ||
| -1 | indicates a cold front approaching | ||
| M030 | 1 | M | S |
| What do you call the area which separates two air masses of different temperature and humidity | |||
| 1 | A front | ||
| -1 | an inversion | ||
| -1 | a trough | ||
| -1 | a rotor | ||
| M031 | 1 | M | S |
| Early in the morning on the ground | |||
| 1 | The dew point and temperature are close together | ||
| -1 | The dew point is higher than the temperature | ||
| -1 | The dew point and the temperature are very far apart | ||
| -1 | The dew point will be always exactly the temperature at sunrise | ||
| M032 | 1 | M | S |
| A flat based cloud, often isolated, with contrasted colors and moderate vertical development is called a | |||
| 1 | Cumulus | ||
| -1 | Lenti | ||
| -1 | Stratus | ||
| -1 | Cirrus | ||
| M033 | 1 | M | S |
| A very high cloud without precipitation, translucent , white, silky, often in form of wisps is called | |||
| 1 | Cirrus | ||
| -1 | Stratus | ||
| -1 | Cumulus | ||
| -1 | Altus | ||
| M034 | 1 | M | S |
| What is the name of the clouds that form beneath thunderstorm clouds and look like cows udders | |||
| 1 | Mammata clouds | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis | ||
| -1 | Nimbostratus | ||
| -1 | NimboCumulus | ||
| M035 | 1 | M | B |
| Turbulence can be caused by | |||
| 1 | Mechanical - trees , mountains,... | ||
| 1 | Thermals - dusties, whirlys, .. | ||
| 1 | Wind shear - different layers of air | ||
| 1 | Vortex by the wing of another aircraft | ||
| -1 | Katabatic airflow in the late afternoon | ||
| -1 | the border between a lake and a wheat field | ||
| -1 | flying over an inversion | ||
| -1 | running too fast at take-off | ||
| M036 | 1 | M | B |
| A mass of cold air advances and repels a mass of warm air by inserting itself underneath the warm air and expelling it upwards | |||
| 1 | This is called a cold front | ||
| -1 | This is called a warm front | ||
| -1 | This is called a trough | ||
| -1 | This is called an occlusion | ||
| M037 | 1 | M | S |
| A Cold front on a synoptic chart is shown | |||
| 1 | in blue with triangles | ||
| -1 | in red with half circles | ||
| -1 | as a green line | ||
| -1 | black curves with numbers | ||
| M038 | 1 | M | S |
| A warm front on a synoptic chart is shown | |||
| -1 | in blue with triangles | ||
| 1 | in red with half circles | ||
| -1 | as a green line | ||
| -1 | black curves with numbers | ||
| M039 | 1 | M | S |
| Bergwind is a wind that | |||
| 1 | Got dried and heated by blowing from a higher area to a lower coastal area | ||
| 1 | is similar to Foehn in the Alpes | ||
| -1 | is caused by mountain slopes cooling down in the late afternoon, creating a downhill breeze | ||
| -1 | is cause by mountain slopes getting warmed up during the day, creating an updraft on the slopes | ||
| M040 | 1 | M | S |
| 13 degree max temperature expected, then this will be a | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Good day - the inversion is not very strong, at 13 degree one is far away from the trigger temperature | ||
| -1 | a poor day - the inversion is far too strong | ||
| -1 | a poor day - 13 degree is simply not enough to create any thermal activity | ||
| -1 | thunderstorm day - the humidity is very close higher up to the lapse rate | ||
| M041 | 1 | M | B |
| What is the name for a cloud that produces hail? | |||
| 1 | Cumulonimbus CB | ||
| -1 | Cumulus | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis | ||
| -1 | Cirrus | ||
| -1 | Stratus | ||
| M042 | 1 | M | S |
| What is the unit to measure cloud cover? | |||
| 1 | The octa - ie an eight of sky covered | ||
| -1 | Millibar | ||
| -1 | Knots | ||
| -1 | Dew points | ||
| -1 | Centigrades | ||
| -1 | Lumen | ||
| -1 | Hectopascal | ||
| M043 | 1 | M | S |
| Warm air sliding up on top of a mass of cold and pushing the cold air in front of it | |||
| 1 | Is called a warm front | ||
| -1 | Is called a cold front | ||
| -1 | Is called a trough | ||
| -1 | Is called a gust front | ||
| -1 | Is called an occlusion | ||
| M044 | 1 | M | S |
| Layer clouds, usually of one colour are called | |||
| 1 | Stratus | ||
| -1 | Cumulus | ||
| -1 | Cirrus | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis | ||
| M045 | 3 | M | S |
| You are flying at 2000m AGL on a great xcountry day in the Highveld. And you got a nice 20 km/h wind pushing from the back. You notice in front, about 1 km ahead, a line of lower clouds developing 1000m below you. Behind that line is no more high cloud. As you approach you have hardly any sink, even some very light lift. Suddenly you are in for some rock and roll. As you cross over that lower line of clouds you loose your glider. After a while you find your glider again in front, or below you, while doing a nosedive towards the ground. Once you rearrange your environment again, that the blue is above and the brown is below, you notice that the 20 km/h back wind has become a 30 km/h headwind. What did you cross through? What is the meteorological term for this? | |||
| 1 | Convergence | ||
| 1 | Boundary of 2 different air masses | ||
| -1 | Inversion | ||
| -1 | Jet stream | ||
| M046 | 1 | M | S |
| An warmed up air parcel leaves the ground at 850 mb level. The T-Phi shows that it will switch from dry adiabatic to wet adiabatic at the 750 mb level. | |||
| 1 | Cloudbase will start around 1000m AGL | ||
| -1 | Cloudbase will start around 1000m ASL | ||
| -1 | Cloudbase will start around 3000m AGL | ||
| -1 | Cloudbase will start around 3000m ASL | ||
| -1 | This question is wrong, the parcel should start at the 750mb level and rise to the 850 mb level | ||
| M047 | 1 | M | B |
| as one gets higher | |||
| 1 | the airpressure drops | ||
| 1 | the temperature tends to drop | ||
| -1 | the airpressure increases | ||
| -1 | the temperature increases | ||
| M048 | 1 | M | S |
| What do we call an airmass, where the temperature increases with altitude | |||
| 1 | An inversion | ||
| -1 | Dry adiabatic lapse rate | ||
| -1 | Wet adiabatic lapse rate | ||
| -1 | Convergence layer | ||
| -1 | A NimboCumulus | ||
| M049 | 1 | M | S |
| What does the prefix 'alto' mean in cloud classification | |||
| 1 | the cloud is in the medium altitude layer from 3500m to 7500m ASL | ||
| -1 | The cloud is touching the ground | ||
| -1 | The cloud contains ice crystals | ||
| -1 | The cloud goes from around 2000m all the way to the stratosphere | ||
| M050 | 1 | M | S |
| what does Cirrus mean in the cloud classification | |||
| 1 | A high altitude cloud found between 7500m and 12000m | ||
| -1 | A dark wet cloud | ||
| -1 | A low level cloud | ||
| -1 | A lens like shaped high cloud | ||
| M051 | 1 | M | S |
| what is an adiabatic process | |||
| 1 | When air changes temperature through compression or expansion without the addition or subtraction of outside heat | ||
| 1 | When warmed up air rises in a thermal | ||
| 1 | When air flows over a mountain and gets pushed down to lower levels | ||
| 1 | When air is pushed up a mountain range | ||
| -1 | When air gets cooled down to dewpoint and the condensating vapor releases heat | ||
| -1 | when paragliding cloth gets coated with silicon to reduce porosity | ||
| -1 | when air gets warmed up on the ground to reach trigger temperature | ||
| -1 | when lines get stretched after they got wet | ||
| -1 | The gadget that one puts on a wing to measure porosity | ||
| M052 | 1 | M | S |
| Unstable air... | |||
| 1 | Has a lapse rate greater than the dry adiabatic lapse rate of 1 Degree per 100m | ||
| -1 | Has a lapse rate that is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate of 1 Degree per 100 m | ||
| -1 | Gets warmer as one gets higher | ||
| -1 | Condensates by 1 degree per 100 m | ||
| M053 | 1 | M | S |
| A stationary cloud above a mountain top could indicate .. | |||
| 1 | Convergence occuring when 2 different air masses from either side of the mountain | ||
| -1 | Strong wind blowing over the crest of the mountain in unstable conditions | ||
| -1 | Wave conditions combined with unstable air | ||
| -1 | A banner cloud, snow fall is possible | ||
| M054 | 1 | M | S |
| Blue thermals ... | |||
| 1 | form in dry conditions with a low dew point | ||
| -1 | form in dry conditions with a high dew point | ||
| -1 | form in stable conditions | ||
| 1 | form in unstable conditions | ||
| M055 | 1 | M | S |
| How high does a thunderstorm go in South Africa | |||
| 1 | around 12-15 km | ||
| 1 | up to the Tropopause | ||
| -1 | about 4 km | ||
| -1 | up to the Stratopause | ||
| M056 | 1 | M | B |
| An anvil is ... | |||
| 1 | part of a thunderstorm cloud | ||
| -1 | part of an altocumuls castellanus cloud | ||
| -1 | a typical shape of a wave cloud | ||
| -1 | a sign for a rotor cloud | ||
| M057 | 1 | M | S |
| When can thermals occur over water? | |||
| 1 | If the water is warmer than the air above it | ||
| -1 | When the water is colder than the air above it | ||
| -1 | Only at night when the sea breeze reverses | ||
| -1 | Only when there is bergwind conditions at the coast | ||
| M058 | 1 | M | S |
| On a flat country shape with no wind, what thermal distribution can one expect | |||
| 1 | A Hexagonal, bee hive, pattern | ||
| -1 | Cloudstreets | ||
| -1 | wave pattern | ||
| -1 | grid pattern | ||
| M059 | 1 | M | B |
| Isobars are ... | |||
| 1 | Lines of the same pressure on a synoptic chart | ||
| -1 | Stiffeners put into the cells of a canopy for a better aerodynamic shape | ||
| -1 | Curves on a map indicating the same altitude | ||
| -1 | Energy food sticks for cross country pilots | ||
| M060 | 1 | M | S |
| A cold front in SA tends to .. | |||
| 1 | Travel from South to North | ||
| 1 | Create strong winds and high seas along the Cape Coast | ||
| -1 | Creates good flying conditions | ||
| -1 | Travel from North to South | ||
| M061 | 1 | M | S |
| When a cold front travels in winter across South Africa | |||
| 1 | The wind tends to turn West before it and swings S for a short time once it passes through | ||
| -1 | The wind tends to turn N before it and then swings to East | ||
| 1 | The wind tends to pick up in front of it | ||
| -1 | The wind tends to become less as it approaches | ||
| M062 | 1 | M | S |
| By how much does the atmospheric pressure change as you rise 100 meters | |||
| 1 | it drops by 1 millibar or 12 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| -1 | it drops by 5 millibar or 60 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| -1 | it drops by 100 millibar or 1200 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| -1 | stays constant | ||
| -1 | it increases by 1 millibar or 12 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| -1 | it increases by 5 millibar or 60 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| -1 | it increases by 100 millibar or 1200 hectoPascal per 100 meters altitude gain | ||
| M063 | 1 | M | B |
| Cumulus Clouds get created by | |||
| 1 | Warmed up air rising and the water vapor in it condensating | ||
| -1 | By the pressure change at the inversion layer causing condensation | ||
| -1 | Katabatic air flow during the day | ||
| -1 | Strong higher up winds creating friction which causes the pressure to drop and initiate condensation | ||
| M064 | 1 | M | B |
| A Thermal is ... | |||
| 1 | a packet of warm air rising into the air | ||
| -1 | an eddy of air in the lee of a ridge | ||
| -1 | air getting pushed over an obstacle | ||
| -1 | an instrument that shows if you go up or down | ||
| M065 | 1 | M | S |
| What can one determine from this block diagram? | |||
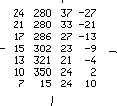 |
|||
| 1 | The air is quite stable | ||
| -1 | The air is quite unstable | ||
| 1 | The lower winds are around North | ||
| 1 | The lower winds are quite strong | ||
| 1 | Not a good day to go Paragliding | ||
| -1 | The lower winds are around East | ||
| -1 | The lower winds are around West | ||
| -1 | The lower winds are around 24 km/h, ok for flying | ||
| -1 | It is a good day to go Paragliding | ||
| M066 | 1 | M | S |
| What can you determine form this picture? | |||
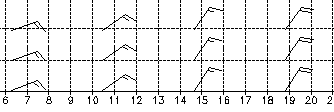 |
|||
| 1 | The wind is swinging during the day from NE to more Northerly | ||
| -1 | The wind is swinging during the day from SW to more Southerly | ||
| 1 | The wind will pick up in the evening to 36 km/h | ||
| -1 | The wind will increase in the evening to 20 km/h | ||
| 1 | The wind will increase in the evening to 20 knots | ||
| 1 | The wind in the morning is around 15 knots | ||
| -1 | The wind in the morning is 15 km/h | ||
| -1 | The wind in the morning is South West | ||
| M067 | 1 | M | S |
| What does this picture show ...? | |||
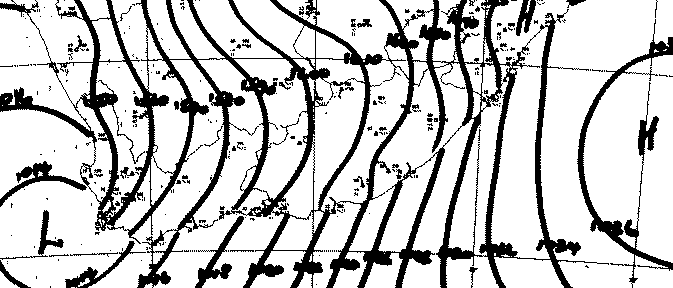 |
|||
| 1 | This is a synoptic chart | ||
| -1 | This is a T-Phi diagram | ||
| 1 | This shows bergwind along the coast | ||
| -1 | This shows on shore flow along the coast | ||
| 1 | A lousy day for going flying | ||
| 1 | Strong winds everywhere | ||
| -1 | Great cross country flying | ||
| -1 | Good flying in Cape Town at Lions Head | ||
| M068 | 1 | M | S |
| What does this picture show ...? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A wave cloud | ||
| 1 | A Lenticularis Cloud | ||
| 1 | Strong winds higher up | ||
| 1 | Possibility of strong turbulence | ||
| -1 | Good thermal activity below the cloud | ||
| -1 | Smooth cross country flying conditions | ||
| -1 | A Cumulus cloud | ||
| -1 | A Nimbo Cumulus cloud | ||
| -1 | A Stratus Cloud | ||
| M069 | 1 | M | S |
| What type of cloud is this and what can we expect later in the day? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | This shows Altocumulus Castellanus | ||
| 1 | One can expect thunderstorms later on | ||
| -1 | This shows Nimbocumulus clouds | ||
| -1 | This shows Lenticularis clouds | ||
| -1 | This shows Stratus clouds | ||
| -1 | Waveconditions later on | ||
| www.wolkenatlas.de | |||
| M070 | 1 | M | S |
| What does this picture show? | |||
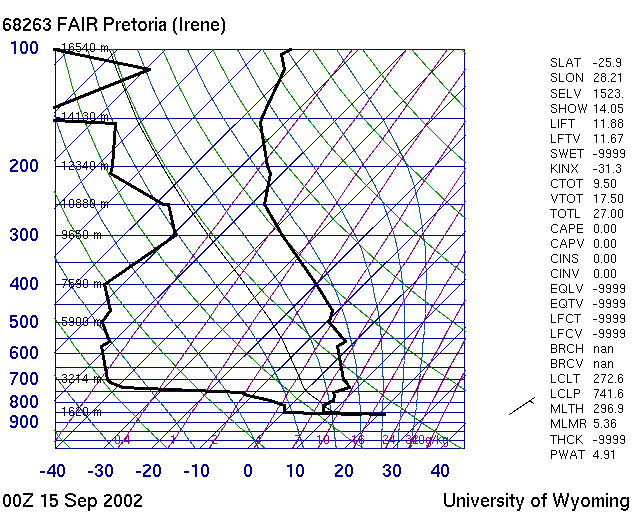 |
|||
| 1 | A faulty Weatherballoon sounding | ||
| -1 | 2 GPS tracks | ||
| -1 | A polar of a wing | ||
| -1 | A Barograph recording of a flight | ||
| -1 | A good day T-Phi Diagram | ||
| -1 | A humid day Skew-T diagram | ||
| The Atmosphere and Weather of Southern Africa | |||
| M071 | 1 | M | S |
| What does this picture show? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A banner cloud | ||
| 1 | Indication that the wind is blowing quite strong from right to left | ||
| -1 | A strong thermal to the left of table mountain | ||
| -1 | The wind is from the left to the right | ||
| Understanding the Sky | |||
| M072 | 1 | M | S |
| What does this picture show? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Cirrus clouds | ||
| 1 | An indication that the wind can get stronger during the day | ||
| -1 | An indication that the wind will get less during the day | ||
| -1 | Stratus Clouds | ||
| -1 | Lenti clouds | ||
| 1 | An indication that there is a cold front approaching | ||
| -1 | An indication that there is a warm front approaching | ||
| -1 | An indication for a trough axis higher up | ||
| Understanding the Sky | |||
| M073 | 1 | M | S |
| FAJS 050700Z 35019KT 1200 -DZ OVC003 11/11 Q1028 TEMPO 3000 BKN008= | |||
| 1 | This is a METAR | ||
| 1 | windstrength is around 34 km/h | ||
| -1 | This is a TAF | ||
| -1 | This is a flightplan | ||
| -1 | This is an SMS from a GPS | ||
| 1 | This was done at the 5th of the month a 09 local SA time | ||
| -1 | whatever it is, it was done 5th of July 2000 at 12.00 | ||
| -1 | This is a Balloon sounding record | ||
| http://aviation.weathersa.co.za | |||
| M074 | 1 | M | B |
| Take Off is facing West. Late afternoon. The smoke of a fire on the opposite slope used to go up during the whole day. Now the smoke is running down the slope into the valley | |||
| 1 | Indication of Katabatic Airflow | ||
| 1 | The opposite slope is now in the shade and the ground is cooling down | ||
| 1 | Since take off is still getting sun shine we could get some valley release | ||
| -1 | Indication of Bergwind | ||
| -1 | Indication of Anabatic air flow | ||
| -1 | Indidcation of Rotor on the opposite slope | ||
| -1 | Indication of the wind picking up and pushing down the smoke flat | ||
| -1 | The smoke is too cold to lift in the warm air of the east ridge | ||
| M075 | 1 | M | S |
| Why does a Lenticularis cloud stays steady | |||
| 1 | The air current flow through the cloud. at the luv side is condesation. at the lee the cloud disolves | ||
| -1 | Lenti clouds move like any other cloud | ||
| -1 | The rotor below the lenti stabilizes the cloud | ||
| -1 | The rotor below creates a low pressure suction which causes the condensation that we see as a lenti | ||
| Understanding the Sky | |||
| M076 | 1 | M | S |
| Gariep in December. Dew point is 17, max expected temperature is 24. | |||
| 1 | Will be a good flying day | ||
| 1 | expected cloud base around 700 meters above ground | ||
| -1 | Will be a good flying day | ||
| -1 | expected cloudbase will be around 1700 meters | ||
| www.paragliding.co.za/sahpa/programs/skygod | |||
| M077 | 1 | M | S |
| It looks very humid in Gariep, in the center of the Free state , in December | |||
| 1 | Better flying with a higher cloudbase can be found towards Beaufort West, towards the South | ||
| -1 | Better flying and cloudbase towards Johannesburg | ||
| -1 | More humid air and worse flying towards the South | ||
| 1 | Find more humid air and worse flying towards the North | ||
| www.paragliding.co.za/sahpa/programs/skygod | |||
| M078 | 1 | M | B |
| Thermals tend to be stronger | |||
| 1 | In Summer due to the earlier sunrise | ||
| -1 | In Winter due to the earlier sunrise | ||
| -1 | In summer due to the later sunrise | ||
| -1 | In Winter due to the earlier sunrise | ||
| M079 | 1 | M | B |
| Cloud coverage is showing 8 octas on a synoptic chart | |||
| 1 | Poor Thermal activity can be expected | ||
| -1 | Good Thermal activity can be expected | ||
| -1 | It is a clear day, no clouds | ||
| -1 | Blue Thermal activity can be expected | ||
| M080 | 1 | M | S |
| Conditions for wave are | |||
| 1 | stable air | ||
| -1 | unstable air | ||
| 1 | wind speed increases with altitude | ||
| -1 | wind speed stays constant with altitude | ||
| -1 | wind speed drops with altitude | ||
| 1 | a mountain range across the wind direction | ||
| -1 | a mountain range parallel with the wind direction | ||
| M081 | 1 | M | S |
| The wind is very strong from the south, driving 1 km North there is no wind, and a further 1km onwards the wind is coming from the North. There are some very high , thin cumulus clouds developing above you. | |||
| 1 | You are in a convergence zone | ||
| -1 | A typical example of catabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | A typical example of anabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | A typical indication for wave development | ||
| -1 | You are in the core of beginning cumulonimbus | ||
| M082 | 1 | M | S |
| The wind is blowing down from the mountain into Porteville at lunch time. And it is very hot. | |||
| 1 | Bergwind and forget about flying for the day | ||
| -1 | Bergwind and indication for a good flying day | ||
| -1 | Good flatland thermal development due to adiabatic compression | ||
| -1 | Strong anabatic airflow, will reverse during the day to become katabatic | ||
| M083 | 1 | M | S |
| Your flying site is dead center in the middle of a High Pressure system | |||
| 1 | Expect a light and variable no wind day | ||
| -1 | Expect Northerly wind | ||
| -1 | Expect Southerly wind | ||
| -1 | Expect Easterly wind | ||
| -1 | Expect Westerly wind | ||
| M084 | 2 | M | S |
| Which of the following staments are correct for this picture? | |||
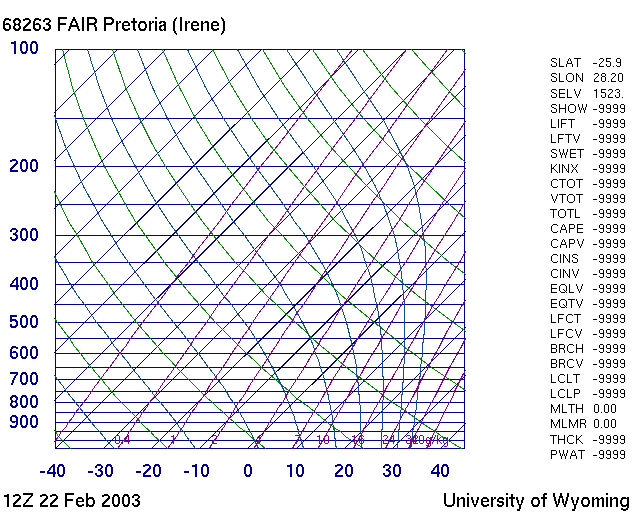 |
|||
| 1 | This is a SkewT Diagram | ||
| -1 | This is a Stueve Diagram | ||
| 1 | Green curves are dry adiabats | ||
| -1 | Purple curves are dry adiabats | ||
| -1 | Green curves are wet adiabats | ||
| 1 | Purple curves are wet adiabats | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/sahpa/programs/skygod/Weather/Sounding.htm | |||
| M085 | 2 | M | S |
| Which of the following staments are correct for this picture? | |||
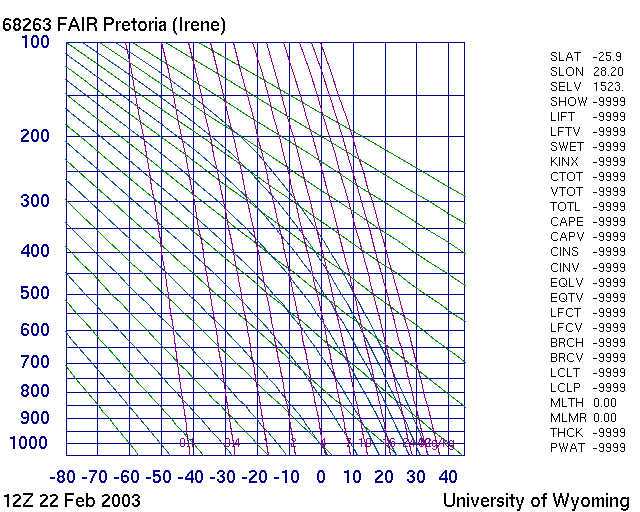 |
|||
| -1 | This is a SkewT Diagram | ||
| 1 | This is a Stueve Diagram | ||
| 1 | Green curves are dry adiabats | ||
| -1 | Purple curves are dry adiabats | ||
| -1 | Green curves are wet adiabats | ||
| 1 | Purple curves are wet adiabats | ||
| http://www.sahpa.co.za/sahpa/programs/skygod/Weather/Sounding.htm | |||
| M086 | 1 | M | S |
| A KINX of 30 or more indicates | |||
| 1 | a good chance for a thunderstorm in sounding data | ||
| -1 | a good glide ratio for a Paraglider on a polar | ||
| -1 | a good aerobatics wing | ||
| -1 | stable air, not much lift for the day | ||
| M087 | 1 | M | S |
| A LIFT Index below 10 and a K below 10 indicates | |||
| 1 | a good XC day in sounding data | ||
| -1 | a poor XC day in sounding data | ||
| -1 | a good wing for thermalling | ||
| -1 | a good glide ratio for a wing | ||
| M088 | 1 | M | S |
| How is an inversion displayed in a synoptic chart? | |||
| 1 | One can not see an Inversion in a synoptic chart | ||
| -1 | in blue with triangles | ||
| -1 | in red with half circles | ||
| -1 | as a green line | ||
| -1 | black curve with numbers | ||
| M089 | 1 | M | B |
| With altitude the wind strength tends to | |||
| 1 | get stronger and this is called windgradient | ||
| -1 | get stronger and this is called windshear | ||
| -1 | get stronger in this is called convergence | ||
| -1 | get less and this is called windgradient | ||
| -1 | get less and this is called windshear | ||
| -1 | get less and this is called convergence | ||
| -1 | get strongers and this is called compression | ||
| -1 | get less and this is called compression | ||
| M090 | 1 | M | B |
| Windshear is defined as | |||
| 1 | a sudden change of wind speed and direction over altitude | ||
| -1 | the turbulence behind an obstacle | ||
| -1 | the increased windspeed in the lee of a hill | ||
| -1 | the late afternoon switchover from anabatic to katabatic wind | ||
| M091 | 1 | M | B |
| What are signs of windshear | |||
| 1 | smoke as it goes up changes direction | ||
| 1 | a smooth thermal suddenly gets ripped apart | ||
| 1 | your drift changes | ||
| -1 | the left side of your wing gets lifted up | ||
| M092 | 1 | M | B |
| Paragliders and Hang Gliders are flying in the | |||
| 1 | Troposphere | ||
| -1 | Stratosphere | ||
| -1 | Mesosphere | ||
| -1 | Exosphere | ||
| M093 | 1 | M | S |
| Watervapor is | |||
| 1 | lighter than air | ||
| -1 | heavier than air | ||
| 1 | makes air release earlier | ||
| -1 | delays the release of warmed up air | ||
| M094 | 1 | M | S |
| Air consists out of | |||
| 1 | 78 percent Nitrogen and 20 percent Oxygen | ||
| -1 | 78 percent Oxygen and 20 percent Nitrogen | ||
| -1 | 78 percent Oxygen and 20 percent water vapor | ||
| -1 | 78 percent water vapor and 20 percent Oxygen | ||
| M095 | 1 | M | S |
| Cumulus Clouds are | |||
| 1 | condensated water vapor | ||
| -1 | water vapor | ||
| -1 | ice crystals | ||
| -1 | small ice pellets | ||
| M096 | 1 | M | S |
| Condensation occures | |||
| 1 | when the temperature falls below the dewpoint | ||
| -1 | when the temperature is higher than the dewpoint | ||
| -1 | when the air temperature reaches the trigger point | ||
| -1 | when the air temperature goes below 0 degree Celcius | ||
| M097 | 1 | M | S |
| Spread is an expression for | |||
| 1 | the difference between surface temperature and dew point on the ground | ||
| -1 | the difference between trigger temperature and dew point at cloud base | ||
| -1 | for the distance setting in the tandem spreader bar | ||
| -1 | what you get in your sandwich in a Cat 1 event lunch pack | ||
| M098 | 1 | M | S |
| A low Spread indicates | |||
| 1 | a low cloudbase for the day | ||
| -1 | a high cloudbase for the day | ||
| -1 | an uncomfortable flight for the tandem pilot | ||
| -1 | Cat 1 event organizers are saving money by introducing lunch pack budget cuts | ||
| M099 | 1 | M | S |
| Superadiabatic means | |||
| 1 | a very high lapse rate | ||
| -1 | a very low lapse rate | ||
| -1 | the airflow on a wing close to stall point | ||
| -1 | the effects on the human body at high altitude due to lack of oxygen | ||
| M100 | 1 | M | S |
| If the temperature of the surrounding air does not change with alitude ... | |||
| 1 | then we got an isothermal layer | ||
| -1 | then we got a superadiabatic layer | ||
| -1 | then we got an inversion layer | ||
| -1 | then we got a standard lapse rate | ||
| M101 | 1 | M | S |
| DALR is around | |||
| 1 | 1 degree Celcius per 100 meters | ||
| -1 | 3 degree Celcius per 100 meters | ||
| -1 | 1013 hPa | ||
| -1 | 1013 millibars | ||
| M102 | 1 | M | S |
| SALR is around | |||
| 1 | .05 degree Celcius per 100 meters | ||
| -1 | 1 degree Celcius per 100 meters | ||
| -1 | 3 degree Celcius per 100 meters | ||
| -1 | 1013 millibars | ||
| M103 | 1 | M | S |
| Stable air ... | |||
| 1 | cools slow with height and vertical movement is limites | ||
| -1 | cools fast with height and vertical movement is plenty | ||
| -1 | cools slow with height and vertical movement is plenty | ||
| -1 | cools fast with height and vertical movement is limites | ||
| M104 | 1 | M | S |
| The CAPE value in a T-phi diagram ... | |||
| 1 | gives an indication for thunderstorms | ||
| -1 | gives an indication what the weather will be like at the cape | ||
| -1 | is used to give an idea how big the waves will be at the cape | ||
| -1 | determines the severity of any squall line | ||
| M105 | 1 | M | S |
| What is the colored area indicating in this picture? | |||
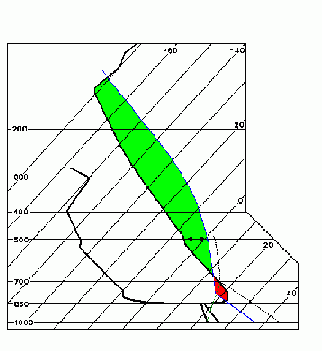 |
|||
| 1 | gives an indication for the chance to have thunderstorms | ||
| 1 | the area relates to the CAPE value | ||
| -1 | how good a wing is for aerobatics | ||
| -1 | the energy in a wing, how docile or wild a wing will react | ||
| M106 | 1 | M | S |
| What cloud is this and what does it indicate? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Bannercloud | ||
| 1 | strong wind blowing from the right | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis | ||
| -1 | wind from the left causing condensation | ||
| -1 | Katabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | Anabatic airflow | ||
| M107 | 1 | M | B |
| What cloud is this and what does it indicate? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Anvil | ||
| 1 | Danger, strong lift underneath it | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis | ||
| -1 | Bannercloud | ||
| -1 | Cumulus | ||
| -1 | Good lift, easy flying conditions | ||
| M108 | 1 | M | B |
| What is a trough ? | |||
| 1 | a sort of low pressure system that appears in SA in summer | ||
| -1 | a paraglider harness piece of equipment | ||
| -1 | a groundshape which acts as a trigger for thermals | ||
| -1 | a gustfront linked with a thunderstorm | ||
| M109 | 1 | M | B |
| Where gets caused by the Coriolis effect? | |||
| 1 | It turns the wind direction during the day | ||
| -1 | It creates the lift over a wing | ||
| -1 | It manages to lock a paraglider in a spiral | ||
| -1 | It creates blurred vision by the lack of oxygen at high altitude | ||
| M110 | 1 | M | B |
| Wind blowing from Cape Town towards Gauteng | |||
| 1 | gets deflected westwards due to the Coriolis effect | ||
| -1 | gets deflected eastwards due to the Coriolis effect | ||
| -1 | gets slowed down due to the Coriolis effect | ||
| -1 | gets accelerated due to the Coriolis effect | ||
| M111 | 1 | M | B |
| The wind on takeoff is 360 and 10 knots. What will the wind probably be higher up ? | |||
| 1 | more easterly | ||
| -1 | more westerly | ||
| 1 | stronger | ||
| -1 | weaker | ||
| M112 | 1 | M | B |
| A jet stream | |||
| -1 | creates vortex turbulence behind an aircraft | ||
| -1 | requires that one first has to get into the wave underneath it | ||
| 1 | can cause thunderstorms in the highveld by sucking up moist air from below | ||
| -1 | is part of a coastal squall line | ||
| M113 | 1 | M | S |
| Which lift processes can form clouds | |||
| 1 | convection | ||
| 1 | fricational turbulence | ||
| 1 | orographic ascent | ||
| 1 | convergence | ||
| M114 | 1 | M | S |
| The air in a thermal cools down by | |||
| 1 | 3 degrees Celcius per 1000 feet | ||
| -1 | 1 degree Celcius per 1000 meter | ||
| 1 | roughly 1 degree Celcius per 100 meter | ||
| -1 | 1 degree Celcius per 300 meters | ||
| M115 | 1 | M | S |
| Clouds form | |||
| 1 | at the convection condensation level | ||
| -1 | at the inversion | ||
| 1 | when the air cools down to dew point | ||
| -1 | only during the day | ||
| M116 | 1 | M | S |
| Which clouds are most likely to generate turbulence | |||
| 1 | Cu,TCu,Cb | ||
| -1 | St | ||
| -1 | Ci,Cs,Cc,Ac,As | ||
| -1 | Sc | ||
| -1 | Ns | ||
| M117 | 1 | M | S |
| Anabatic describes | |||
| 1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows up the slope during due to heating of the slopes | ||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows downhill due to heating of the slopes | ||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows up the slope due to cooling of the slopes | ||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows downhill due to cooling of the slopes | ||
| -1 | low oxygen in the blood and a pale skin color | ||
| -1 | cold air from the sea getting sucked in by warmed up air inlands | ||
| M118 | 1 | M | S |
| Katabatic describes | |||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows up the slope due to heating of the slopes | ||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows downhill due to heating of the slopes | ||
| -1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows up the slope due to cooling of the slopes | ||
| 1 | a local wind system, where the wind blows downhill due to cooling of the slopes | ||
| -1 | low oxygen in the blood and a pale skin color | ||
| -1 | cold air from the sea getting sucked in by warmed up air inlands | ||
| M119 | 1 | M | S |
| What does DALR stand for? | |||
| 1 | Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate. | ||
| 1 | The change in temperature of an air parcel as it is lifted | ||
| -1 | The German Department for Aviation and Space ,Deutsche Abteilung fuer Luft und Raumfahrt | ||
| -1 | Department of Aviation Legal Regulations | ||
| M120 | 1 | M | S |
| During Winter in South Africa | |||
| 1 | we got a High Pressure System in the center of the country | ||
| -1 | we got a Low Pressure System in the center of the country | ||
| 1 | we can expect no wind to light and variable winds | ||
| -1 | we can expect strong winds | ||
| M121 | 1 | M | S |
| A sounding states 00Z | |||
| 1 | This means it was done at 2 in the morning in South Africa | ||
| -1 | This means it ws done at midnight at station Z in South Africa | ||
| -1 | It means that is the center rib cross section of a wing | ||
| -1 | It means the track log has not been scored yet in RACE | ||
| M122 | 1 | M | S |
| Trigger temperature ... | |||
| 1 | defines the temperature on the ground when one can expect the start of thermal activity | ||
| -1 | gets reached in a rising airpacket when the air has cooled down to create condensation | ||
| -1 | states how much air has to cool down beyond freezing point to create hail | ||
| -1 | gets reached when the rising air cools down to dew point | ||
| M123 | 1 | M | B |
| Light Northerly at The Dam. Thunderstorms to the South. Now the wind dies and swings South. | |||
| 1 | Gustfront approaching, caused by the Thunderstorms to the South | ||
| -1 | Typical valley release for The Dam | ||
| -1 | Local wind system switching to Katabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | The wind always switches South in the afternoon at The Dam | ||
| M124 | 1 | M | B |
| A Gustfront ... | |||
| 1 | means strong wind and a rough ride for anyone who is still in the air | ||
| -1 | is the only way how one can fly big distance | ||
| -1 | is nothing to worry about | ||
| -1 | is extremely small and can be ignored | ||
| M125 | 1 | M | S |
| The wind at take-off is over the back, while the wind in the valley is towards take-off. And there is clouds forming in front of take-off. Those who managed to take-off earlier are having good flying under those clouds. | |||
| 1 | Indication for a convergence | ||
| -1 | those are rotor clouds | ||
| -1 | the clouds are cirrus clouds | ||
| -1 | this is called cloudsuck | ||
| M126 | 1 | M | S |
| Soarcast gives 3 knots lift for the day | |||
| 1 | a weak 1.5 m/s max thermal day | ||
| -1 | a 6 m/s strong thermal day | ||
| -1 | knots can not be used for thermal strength | ||
| -1 | a 3m/s thermal day | ||
| http://home.att.net/~doug.kathy/Soarcast/Download.htm | |||
| M127 | 1 | M | B |
| Medium level clouds are called | |||
| -1 | cirrus | ||
| 1 | Alto- like Altostratus, Altocumulus | ||
| -1 | Strato- like stratocumulus | ||
| -1 | Nimbo- like Nimbo stratus | ||
| M128 | 1 | M | B |
| The 3 stages of a thunderstorm are | |||
| 1 | convection, cumulus, mature | ||
| -1 | mature, advection,towering | ||
| -1 | cumulus,advection,dissipating | ||
| -1 | gustfront, mamata, cumulus | ||
| M129 | 1 | M | S |
| Explain this ....??? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Approaching gust front, do not fly | ||
| -1 | ... put that away or get struck by lightning | ||
| -1 | an example of what electrical fields before a storm can do to you | ||
| -1 | example of what a bad fitting harness can do to a male | ||
| http://www.schlechtflieger.de | |||
| M130 | 1 | M | S |
| FAJS 230400Z 08004KT 2500 BR BKN110 17/15 Q1027 TEMPO 1500 BCFG SCT008= | |||
| -1 | it is raining already | ||
| 1 | poor day, dew point and temperature are close together, early thunderstorms | ||
| -1 | blown out, far too strong | ||
| -1 | 23 degree and a dew point of 4, very good thermals | ||
| M131 | 1 | M | S |
| the forecast reckons that the Atlantic High is ridging in over you flying area | |||
| -1 | expect good thermals | ||
| 1 | lots of whirlies, bumpy, stressy flying day, thermals will not go high | ||
| -1 | expect overcast and rain | ||
| -1 | expect thunderstorms | ||
| M132 | 1 | M | S |
| air from the Atlantic High is | |||
| -1 | unstable, because of the cooling down of the lower layers by the cold Benguela stream | ||
| 1 | stable, due to the cooling down of the lower laayers by the cold Benguela stream | ||
| -1 | unstable, because of the warming up of the lower layers by the warm Benguela stream | ||
| -1 | stable, because of the warming up of the lower layers by the warm Benguela stream | ||
| M133 | 1 | M | S |
| From this picture one can figure out ... | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | there will be good lift on every side of the mountain | ||
| 1 | the wind will be far too strong on top to fly | ||
| -1 | it will start snowing soon | ||
| -1 | Aliens are having a base up there | ||
| M134 | 1 | M | S |
| Where would you expect thermals | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | there are no thermals in winter | ||
| 1 | at the edge ofthe snow areas | ||
| -1 | in the center of the valley | ||
| -1 | only on the peaks | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Abrisskanten.223.0.html | |||
| M135 | 1 | M | S |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | low pressure system and warmfront | ||
| 1 | high pressure system and inversion | ||
| -1 | humid inversion | ||
| -1 | catbatic and anbatic air flow | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Absinkinversion.269.0.html | |||
| M136 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows the effects of Albedo, which means | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | unstable humid air shooting up without an inversion stopping it | ||
| 1 | the difference in reflecting sunlight and absorbing solar rays which warms up the ground. Resulting in finding the lift over the exposed rock faces facing the sun. | ||
| -1 | the boundary between humid air in the back and dry air in the front | ||
| -1 | the blue glider looks white , due to blue light getting dispersed with altitude | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Albedo.268.0.html | |||
| M137 | 1 | M | S |
| What are these clouds and what do they indicate | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | Cirrocumulus , a cold front is approaching, dangerous | ||
| 1 | Altocumulus , a warm front is approaching, safe to fly | ||
| -1 | Stratus, an occlusion is coming, will rain soon | ||
| -1 | Cumulus, will be good lift under them | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Altocumulus.267.0.html | |||
| M138 | 1 | M | S |
| What are these clouds and what do they indicate | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Altocumulus Lenticularis, very strong winds higher up | ||
| -1 | Altocumulus Lenticularis, when they stay steady then there is no higher wind | ||
| -1 | Stratus, it will rain soon | ||
| -1 | Cumulus, will be good lift under them | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Altocumulus_Lenticul.266.0.html | |||
| M139 | 1 | M | S |
| What are these clouds and what do they indicate | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Cirrostratus, approaching warmfront about 1000km away, rain in 2 days | ||
| -1 | Cirrostratus, approaching cold front, thunderstorms in a few hours | ||
| -1 | Stratus, cold air gliding on top of warm air, it will rain soon | ||
| -1 | Cumulonimbus ,Overdevelopment, thunderstorm | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Aufgleitbew_lkung.265.0.html | |||
| M140 | 1 | M | S |
| What are these clouds and what do they indicate | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Cumulus clouds stopped by a strong inversion. Spreading out and creating big shadow areas with no lift. | ||
| -1 | Cirrostratus, approaching cold front, thunderstorms in a few hours | ||
| -1 | Stratus, cold air gliding on top of warm air, it will rain soon | ||
| -1 | Cumulonimbus ,Overdevelopment, thunderstorm | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Ausbreitungsschicht.264.0.html | |||
| M141 | 1 | M | S |
| What can one determine from this picture | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Triggertemperature has been reached | ||
| -1 | Stable air, no turbulence | ||
| -1 | Altocumulus Castellanus , early thunderstorms | ||
| -1 | Cumulonimbus ,Overdevelopment, thunderstorm | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Ausl_setemperatur.263.0.html | |||
| M142 | 1 | M | S |
| What statements are true | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A blue thermal day | ||
| -1 | No clouds, no thermals | ||
| -1 | very humid air stops condensation and cloud forming | ||
| 1 | very dry air results in any rising air not reaching dew point | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Blauthermik.262.0.html | |||
| M143 | 1 | M | S |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Sqall line or gust front, do not fly | ||
| -1 | Sqall line or gust front, time to fly | ||
| -1 | katabatic air flow creating fog | ||
| -1 | dry air from an adiabatic air flow disolving morning mist | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/B_enwalze.260.0.html | |||
| M144 | 1 | M | S |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Your shadow on the cloud layer with a halo around it | ||
| -1 | Another paraglider sinking out of the clouds coming towards you | ||
| -1 | What the world looks like in the morning after a good party | ||
| -1 | Smoking while flying impacts on the vision around you | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Brockengespenst.259.0.html | |||
| M145 | 1 | M | S |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Cirrocumulus over Cumulus , which could mean thunderstorms later | ||
| -1 | Stratus clouds, rain later | ||
| -1 | Dry air moving in, will kill all thermals | ||
| -1 | Humid air cold air triggering the altocumulus castellanus clouds | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cirrocumulus.258.0.html | |||
| M146 | 1 | M | S |
| This shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Cirrostratus, strong winds that might come down later | ||
| -1 | Cirrocumulus, snow later | ||
| -1 | Lenticularis, good wave conditions | ||
| -1 | Triggertemperature too low to create proper thermals | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cirrostratus.257.0.html | |||
| M147 | 1 | M | S |
| Those Cirrus clouds | |||
 |
|||
| -1 | will improve the thermal lift later on | ||
| 1 | can delay thermal acitivity and weaken thermal strength | ||
| -1 | will become thunderstorms later on | ||
| -1 | will turn into stratus and create fog | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cirrus.256.0.html | |||
| M148 | 1 | M | B |
| This cloud | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | is a good looking Cumulus, go for it | ||
| -1 | is a dangerous looking cumulus. Thats why the HG turns away from it | ||
| -1 | is not for real, it is a reflection on the inversion layer | ||
| -1 | will turn into stratus and create fog | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cumulus__mediocris_.255.0.html | |||
| M149 | 1 | M | B |
| These clouds indicate | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Altocumulus Castellanus, no inversion, thunderstorms in a few hours, time to land and pack up | ||
| -1 | good lift, time to take off and fly | ||
| -1 | katabatic lift over the mountain range | ||
| -1 | the foehn barrier, humid air getting pushed over the mountains | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cumulus_castellanus.254.0.html | |||
| M150 | 1 | M | B |
| This clouds indicates | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | trouble, land immediatley | ||
| -1 | good lift, time to take off and fly | ||
| -1 | good lift for another hour | ||
| -1 | dying thermal, no lift there | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cumulus_congestus.253.0.html | |||
| M151 | 1 | M | B |
| CB CumuloNimbus Clouds | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | go through all the layers of the Troposhpere | ||
| -1 | go through all the layers of the Stratosphere | ||
| 1 | can be 15km high | ||
| 1 | can cause gustfronts 20-30 km away which make your flying miserable | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Cumulonimbus.252.0.html | |||
| M152 | 1 | M | B |
| What is your next move | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | leave the thermal now before you have to fly through the lower edge of the cloud | ||
| -1 | continue in the 5-8 m/s lift until you loose visibility of the ground | ||
| -1 | switch on your GPS and be ready for some cloud flying | ||
| -1 | agree with the other pilots around you on the thermal direction then go into the cloud | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Domeffekt.251.0.html | |||
| M153 | 1 | M | S |
| this poor visibility is caused by | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | humid air condensing on dust particles | ||
| -1 | dry unstable air which causes an inversion layer | ||
| -1 | the blue light of the sun radiation being absorbed and radiated by the H2O molecules | ||
| -1 | the cloud spitting out surplus condensation paarticles | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Dunst.250.0.html | |||
| M154 | 1 | M | S |
| this shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | humid air condensing on dust particles | ||
| -1 | dry unstable air which causes an inversion layer | ||
| -1 | the blue light of the sun radiation being absorbed and radiated by the H2O molecules | ||
| -1 | the cloud spitting out surplus condensation paarticles | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/F_hn.249.0.html | |||
| M155 | 1 | M | S |
| this shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Foehn in the Alpes, can be dangerous | ||
| -1 | Foehn in the Alpes, which means very good flying | ||
| -1 | the end of a thunderstorm, safe to fly now | ||
| -1 | flat cumulus clouds, not much lift | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/F_hn.249.0.html | |||
| M156 | 1 | M | S |
| Those 2 PG pilots fly so close to the rocks | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | the sun warms up the rock face, generating lift | ||
| -1 | because they are suicidal | ||
| -1 | because they are in rotor otherwise | ||
| -1 | because they just jumped off the cliff | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Herbstthermik.248.0.html | |||
| M157 | 1 | M | B |
| This picture shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A strong ground inversion | ||
| 1 | One can have a long flight above the inversion | ||
| 1 | One requires a landing spot above the inversion | ||
| -1 | The Inversion stops all thermal activity for the day | ||
| -1 | One requires a GPS with a track log to follow to land below the inversion | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Inversionswetterlage.246.0.html | |||
| M158 | 1 | M | B |
| A cold front is approaching. | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | It is caused by cold air lifting up warmer air | ||
| -1 | It is caused by warm air pushing away cold air | ||
| 1 | will cause the temperature to drop | ||
| 1 | will cause the wind to become stronger and turn | ||
| 1 | the safest option for this pilot is to land on the slope now | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Kaltfront.245.0.html | |||
| M159 | 1 | M | S |
| What can you expect under those wisps | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | a very strong thermal | ||
| -1 | a very weak thermal | ||
| 1 | turbulence, since no where else is any similar condensation | ||
| -1 | a rotor from a wave cloud | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Kondensationsfetzen.241.0.html | |||
| M160 | 1 | M | S |
| How did the PG pilot get that high above the cloudbase? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | at takeoff he had a dryer airmass with a higher cloudbase. | ||
| -1 | he jumped out of a balloon | ||
| -1 | this picture was taken from a PPG | ||
| -1 | we are looking at a low inversion layer | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Kondensationsniveau.240.0.html | |||
| M161 | 1 | M | S |
| Which way is the wind blowing and what causes the condensation | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | from left to right | ||
| -1 | from right to the left | ||
| 1 | there is a big rotor which sucks up humid air from the right | ||
| -1 | this is snow getting blown over the edge cooling down the air behind it | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Leefahnen.239.0.html | |||
| M162 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows an example of Lee thermic conditions | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | the thermals come up the sunny slopes and then get shifted by the wind over the back | ||
| 1 | Once one gets up above the ridge it becomes very turbulent | ||
| 1 | The clouds get shifted away from the top of the peaks indicating wind shear | ||
| 1 | the clouds are frazzled, indicating turbulence | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Leethermik.238.0.html | |||
| M163 | 1 | M | S |
| Why is there thermals in the middle of winter? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | because the air has an unstable lapse rate | ||
| -1 | because the air has a stable lapse rate | ||
| 1 | because the tree areas are snow free and warm up a bit more than the snowy areas | ||
| -1 | because the snow warms up the air above it | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Luftschichtung.237.0.html | |||
| M164 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | an example of 2 different airmasses | ||
| -1 | dry air at the horizon, while flying in humid air | ||
| 1 | humid air at the horizon, while flying in dry air | ||
| -1 | flying in anabatic conditions | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Luftmassengrenze.236.0.html | |||
| M165 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Coastal flying, where a cold water current cools down the air above it | ||
| -1 | a cold front approaching | ||
| -1 | a warm front approaching | ||
| -1 | warm humid air condensating at the inversion layer | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Passat.234.0.html | |||
| M166 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows a collapsing Foehn. Expect | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | rain due to the signs of an approaching warm front | ||
| -1 | good flying the next day | ||
| -1 | the Lenti clouds will become bigger | ||
| -1 | the Lenti clouds turn into cumulus clouds | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Pr_frontaler_F_hn.233.0.html | |||
| M167 | 1 | M | B |
| 8 kms short of goal. What is the best option? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | turn around, park under some lift for an hour, then carry on | ||
| -1 | fly through the rain | ||
| -1 | land quickly to avoid the gust fronts | ||
| -1 | go into the cloud and fly over the rain | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Regenschauer.232.0.html | |||
| M168 | 1 | M | B |
| What is this cloud underneath the Lenti cloud? And what does it mean for you as a pilot? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | A Rotor Cloud. Very turbulent and dangerous | ||
| -1 | A Rotor Cloud. Very smooth lift under it | ||
| -1 | A late afternoon last thermal | ||
| -1 | Anabatic airflow creates this condensation cloud | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Rotorwolke.231.0.html | |||
| M169 | 1 | M | B |
| Later afternoon. Where the lift? And why? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | In the middle of the valley. Due to katabatic airflow one can find weak lift. | ||
| -1 | On the shady slopes. Due to the trees releasing the accumulated heat | ||
| -1 | On the sunny slopes. Strong thermals due to anabatic airflow. | ||
| -1 | On the top of the peaks. Due to anabatic airflow. | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Umkehrthermik.228.0.html | |||
| M170 | 1 | M | B |
| What is this on top of the cloud? What is your decision ? | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Ice from humid air moved up very fast and high. Pack up | ||
| -1 | Ice created by good lift. Layout and fly | ||
| -1 | A Lenti. Foehn will stop any overdevelopment. One can fly. | ||
| -1 | A rotor cloud, fly but stay clear of it. | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Vereisung.227.0.html | |||
| M171 | 1 | M | B |
| Here we got a ... | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | cloud street | ||
| -1 | late evening katabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | early morning anabatic airflow | ||
| -1 | weak cold front | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Wolkenstra_en.226.0.html | |||
| M172 | 1 | M | S |
| The rule of thumb to calculate the cloudbase from the spread is | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | cloudbase in meters = 122 x spread | ||
| 1 | cloudbase in feet = 400 x spread | ||
| -1 | cloudbase in meters = 1220 x spread | ||
| -1 | cloudbase in feet = 4000 x spread | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/Wolkenuntergrenze.225.0.html | |||
| M173 | 1 | M | S |
| Cloud Coverage is measured in | |||
| 1 | Octas | ||
| -1 | Degrees | ||
| -1 | feet | ||
| -1 | Lumen | ||
| M174 | 1 | M | S |
| If you want a cloudbase of at least 2000 m ATO and you expect a max temperature of 30 what should the dewpoint be in this Metar? | |||
| 1 | FAWM 140500Z AUTO 15003KT //// // ////// 18/07 Q1020= | ||
| -1 | FAWM 140500Z AUTO 15003KT //// // ////// 18/17 Q1020= | ||
| -1 | FAWM 140500Z AUTO 15003KT //// // ////// 18/27 Q1020= | ||
| -1 | FAWM 140500Z AUTO 15003KT //// // ////// 18/30 Q1020= | ||
| M175 | 1 | M | B |
| This picture shows | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | cloudstreet | ||
| -1 | CB clouds | ||
| -1 | altostratus clouds | ||
| -1 | lenticularis wave clouds | ||
| Oz Report 8 111 Kim Grummitt | |||
| M176 | 1 | M | B |
| If the temperature drops or more humid air will be pushed up from the sea below takeoff ... | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | then the clouds will increase and flying will become dangerous. Expect flying conditions with poor visibility | ||
| -1 | cloud base will raise. Expect ideal flying conditions with good visibility | ||
| -1 | then the lift will improve in these conditions | ||
| -1 | the clouds will disappear | ||
| http://www.dhv.de/typo/T_dlicher_Nebelflug.1708.0.html | |||
| M177 | 1 | M | B |
| This picture shows a... | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Foehn conditions in the Alpes. Flying can be dangerous. | ||
| -1 | Perfect day | ||
| -1 | Cumulus clouds | ||
| -1 | Nimbo cumulus clouds developing | ||
| http://www.flugschule-goeppingen.de/info/service/fachartikel.html | |||
| M178 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows ... | |||
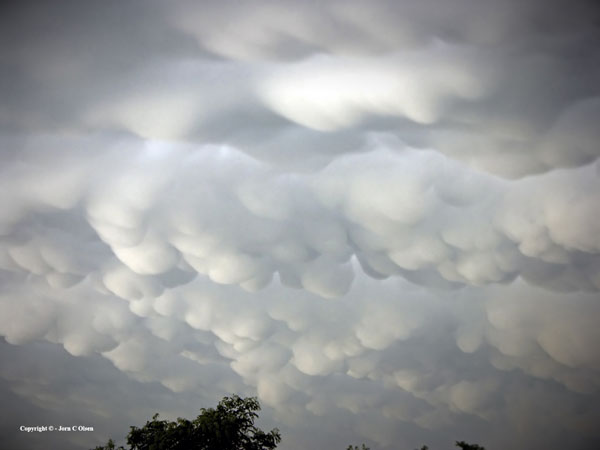 |
|||
| 1 | Mammata clouds. Indicates very unstable air and a thunderstorm close by | ||
| -1 | a morning glory | ||
| -1 | Cumulus clouds | ||
| -1 | Nimbo cumulus clouds developing | ||
| http://jornolsen.com/slidemammatus.html | |||
| M179 | 1 | M | S |
| This picture shows ... | |||
 |
|||
| 1 | Virga. Rain or ice falling out of a cloud. Potential for a gust front | ||
| -1 | A morning glory | ||
| -1 | Cumulus clouds | ||
| -1 | Nimbo cumulus clouds developing | ||
| http://www.wunderground.com/blog/JeffMasters/comment.html?entrynum=1 | |||